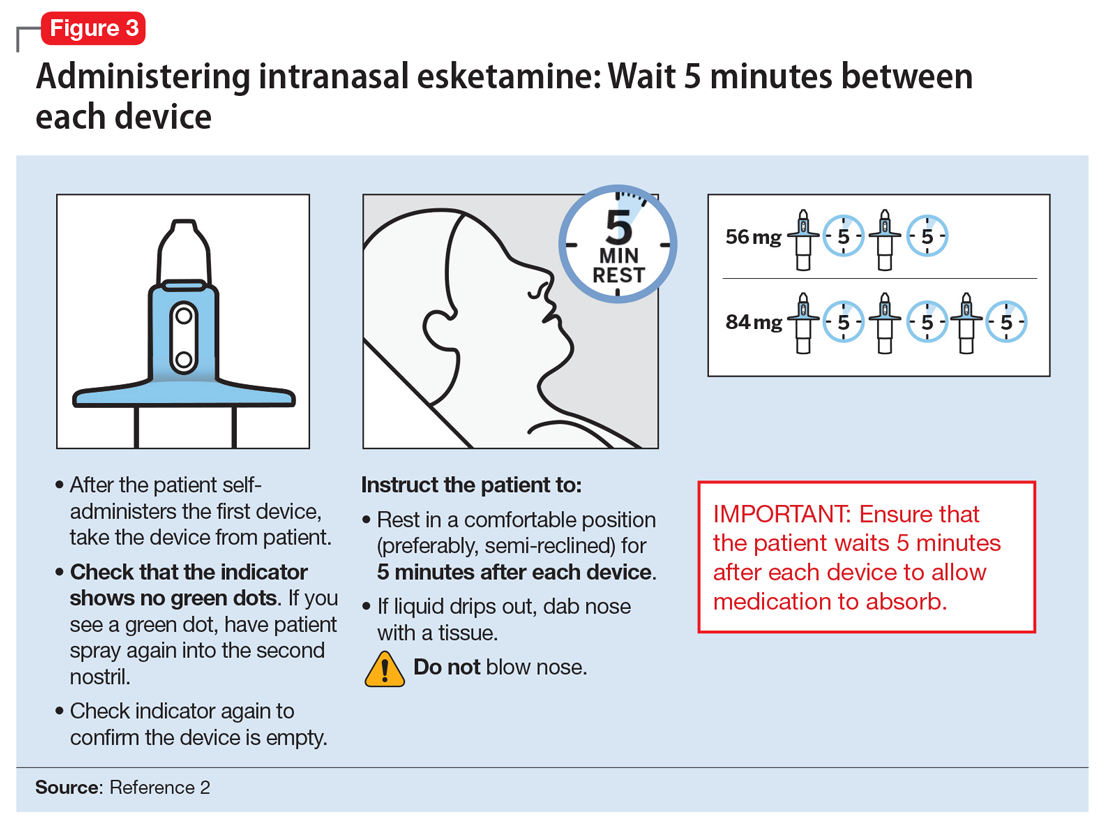
After each intranasal administration the patient will be observed for 5 minutes before the second nasal inhaler is utilized and for another 5 minutes when the patient is receiving 84 mg (ie, each inhaler equals 28 mg). After administering, blood pressure should be reassessed at approximately 40 minutes, which corresponds to the Cmax of intranasal esketamine, and periodically thereafter as warranted.
The patient will then be monitored in a quiet environment for a minimum of 2 hours to make sure that dissociative phenomenon, sedation, and hypertensive reactions have normalized prior to discharge from a certified REMS treatment center.
Dosing and administration
Each intranasal device is primed for 2 infusions (1 in each nostril) for a total dose of 28 mg of esketamine. Combinations of devices can be used to adjust the dose as appropriate for individual patients. The recommended starting dose is 56 mg (ie, 2 devices, with a 5-minute gap between devices). The dose can be increased to 84 mg (ie, 3 intranasal devices spaced at 5-minute intervals) by the second dose based on clinical judgment.
The patient will be instructed to recline the head to a 45° angle, clear his or her nostrils prior to the first treatment, and then self-administer a dose to each nostril while holding the reciprocal nostril closed and inhaling. This process is then repeated every 5 minutes for each subsequent device, with a maximum total dose of 3 devices, or 84 mg (Figure 32). The patient will then be monitored for blood pressure, heart rate, and signs of psychologic or physiologic changes for the next 2 hours. Patients may not drive a car or operate any type of motor equipment until the following day after receiving a normal night’s sleep. Patients will be released from the REMS treatment center after 2 hours if both psychological and physical adverse effects have normalized.
Missed treatment sessions. If a patient misses a treatment session and there is worsening of depressive symptoms, consider returning the patient to the previous dosing schedule (ie, every 2 weeks to once weekly, or weekly to twice weekly).
Continue to: Contraindications for...