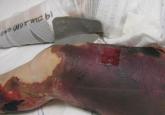
Furthermore, studies have shown that lymphocytes in CD patients display impaired regulatory T-cell function, causing increased incidence of autoimmune diseases and malignancy.7,8 By this theory, the occurrence of MF in patients is facilitated by the inability of CD lymphocytes to control the abnormal T-cell proliferation in the skin. Interestingly, the finding of SS in our patient supports the possibility of impaired regulatory T-cell function.
Although the occurrence of both MF and CD in our patient could be coincidental, the possibility of correlation must be considered as more cases are documented.