In contrast, patients who lose weight by dieting or undergoing gastric restrictive procedures show a modest increase in insulin sensitivity and a compensatory reduction in insulin secretion, termed “beta-cell rest.” 16,31,42
RISKS OF BARIATRIC SURGERY
Short-term risks
An important concern about using bariatric surgery to treat type 2 diabetes is the risk of morbidity and death associated with these procedures.
Buchwald et al 13 performed a meta-analysis of 136 bariatric studies that included 22,094 patients. The 30-day operative death rates were 1.1% with biliopancreatic diversion, 0.5% with Roux-en-Y surgery, and 0.1% with restrictive procedures.
Laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding is considered the safest of the current bariatric procedures. It does not involve bowel anastomosis, and the risks of major hemorrhage, gastric perforation, and pulmonary embolism are less than 1%. Late complications requiring reoperation include band slippage or prolapse (5%–10%) and band erosion (1%–3%). The entire intestinal tract is left intact, so subsequent nutritional deficiencies are rare. 43
Roux-en-Y gastric bypass carries an overall risk of major complications of 10% to 15%. Anastomotic leak (1%–5%), pulmonary embolism (< 1%), and hemorrhage (1%–4%) can be life-threatening but are rare if the staff are experienced. Late complications such as ulcer or stricture formation at the gastrojejunostomy site occur in 5% to 10% of cases and are managed nonoperatively.
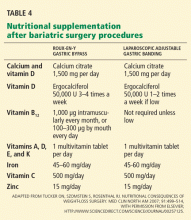
Nutritional deficiencies
Nutritional deficiencies, including proteincalorie malnutrition and deficiencies of iron, other minerals, and vitamins A, E, D, and B 12, occur in 30% to 70% of patients ( Table 3 ). Patients at high risk of developing severe nutritional deficiencies include those who have lost more than 10% of their body weight by 1 month, those with anastomotic stenosis, those undergoing surgical revision, and those with persistent vomiting. 44Protein-calorie malnutrition is recognized by signs such as edema, hypoalbuminemia, anemia, and hair loss. To minimize this problem after Roux-en-Y surgery, we suggest that patients take in 60 to 80 g of protein and 700 to 800 kcal a day.
Vitamin deficiencies can lead to Wernicke encephalopathy (due to thiamine deficiency), peripheral neuropathy (due to vitamin B 12 deficiency), 45,46 and metabolic bone disease (due to long-term deficiencies of vitamin D and calcium). Often, vitamin deficiencies are present before surgery and require prompt supplementation to avoid exacerbation of these deficiencies afterward.
Biliopancreatic diversion procedures are performed at relatively few centers worldwide, largely because of the massive amounts of protein, fat, and carbohydrate malabsorption they cause. Long-term deficiencies of fat-soluble vitamins, iron, calcium, and vitamins B 12 and D have been reported in one-third to one-half of patients undergoing these procedures, and nutritional supplementation is mandatory. 43 Protein-calorie malnutrition occurs in 7% of cases, and 2% of patients require operative revision to lengthen the common channel.
Monitoring of nutrient and vitamin levels after bariatric surgery is recommended at least every 6 months. Table 3 summarizes the nutrient deficiencies to expect after Roux-en-Y surgery; Table 4 lists replacement strategies.In rare cases, severe hypoglycemia has been noted after Roux-en-Y surgery and is associated with prandial hyperinsulinemia related to elevated GLP-1 levels. 36,47 Neuroglycopenia and seizures have been reported in severe cases. Initial treatment of hypoglycemia involves dietary modification targeting carbohydrate restriction, the use of alpha glucosidase inhibitors such as acarbose (Precose), and referral to an endocrinologist for further management.