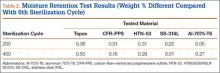
Moisture Retention. Moisture retention was evaluated by weighing the test materials before and after repeated sterilization. There was no significant difference in moisture retention, as weight differences for all the tested materials were less than 0.5 weight percentage compared to the 0th sterilization cycle (Table 2). Therefore, the results of this study showed that all the tested materials exhibited good moisture/temperature resistance after 400 sterilization cycles.
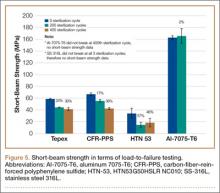
Load to Failure. In the LTF test, significant differences were detected in SBS between all 5 tested materials (P < .05). Figure 5 shows the comparison of the structural properties in terms of SBS between the 5 tested materials, and Figure 6 shows the failure modes for the tested materials. There was no SBS for SS-316L, as the material did not exhibit complete structural failure even after 400 sterilization cycles; however, SS-316L was observed in inelastic deformation failure (Figure 6D). Al-7075-T6 had much higher SBS compared with the other composite materials, and it also resulted in an inelastic deformation failure mode only after 400 sterilization cycles; otherwise, flexure failure modes were observed. Tepex and CFR-PPS exhibited interlaminar shear failure, and HTN-53 exhibited complete structural failure.
Every composite material tested using the short-beam test for LTF showed a decrease in SBS with increased sterilization cycles (Figure 5). This decrease ranged from 17% to 57% compared with the 0th sterilization cycle. SBS was higher for CFR-PPS than for the other 2 composites. No statistically significant difference was found between CFR-PPS and Tepex except at the 200th sterilization cycle. HTN-53 was brittle at the 0th sterilization cycle but performed more like a ductile material at the 200th cycle. In addition, HTN-53 had the lowest SBS in terms of LTF testing when compared with the other 2 composites.
During the complete structural failure test, the failure modes for Tepex and CFR-PPS were visually identified as interlaminar shear failure (Figures 6A, 6B), whereas HTN-53 visually exhibited pure flexure failure (Figure 6C). As for the metals, SS-316L exhibited plastic deformation, and Al-7075-T6 exhibited flexure failure (Figures 6D, 6E).
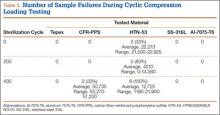
Cyclic Compression Loading. Tepex was the only material to pass the 100,000 loading cycle without failure (Table 3). HTN-53 had the poorest performance of all: Its failure rates were 33% (2/6 samples) before sterilization (average cycle, 22,213; range, 21,500-22,925), 83% (5/6 samples) at the 200th sterilization cycle (average cycle, 4,210; range, 0-14,360), and 100% after 400 sterilization cycles (average cycle, 12,725; range, 1,190-21,900). CFR-PPS had no failures before the 400th sterilization cycle, and its failure rate after 400 sterilization cycles (average cycle, 50,735; range, 50,270-51,200) was 33% (2/6 samples).
Discussion
The success of a reusable composite material for use in orthopedic surgery depends not only on radiographic density, fabrication methods, and design but also on the ability to withstand repeated sterilization. Over the past 3 decades, investigators have explored several high-performance polymer matrix composite materials for use in orthopedics, especially in trauma, hip stems, and spinal implants.1,3,4,17-34 According to Evans and Gregson,35 composite materials have been widely promoted as possible orthopedic biomaterials but to date have found few successful commercial applications, because of the many challenging problems encountered in fabrication and testing. One of the most important factors in the mechanical properties of many composite materials is the influence of the cooling and loading rates on fiber-matrix interface adhesion.36-38 Our results tended to agree with the findings of Evans and Gregson,35 as some of these composite materials did not withstand repeated sterilizations well.
Guan and colleagues39 evaluated the influence of sterilization treatment on continuous carbon-fiber–reinforced polyolefin composite. Their 3-point bending test results showed that the levels of maximum load of all the specimens undergoing sterilization by autoclave were lower than those of the control group. For these composites, they concluded that autoclave sterilization and Co-60 gamma ray irradiation sterilization should be avoided and that ethylene oxide is the best method. Our results support their findings with a different set of composites.
Although HTN-53 has shown promise in other orthopedic applications because of its superior moisture and temperature resistance, we found that its performance after repeated sterilization was relatively poor. Tepex showed the greatest potential for durability after repeated sterilization; its mechanical properties were stable after 200 steam sterilization cycles.
Clinical Applications
The composite materials investigated in the present study have potential for use in either instrumentation or long-term implantation applications because of their versatility, mechanical strength, fatigue resistance, and biocompatibility. Akay and Aslan40 stated that carbon-fiber–filled composite implants can be designed with more appropriate modulus, strength, toughness, or stiffness by the arrangement of reinforcing fiber volume and orientation, and can provide better fatigue resistance. A notable advantage of using a composite plate with metal screws is that the potential for corrosion of metallic components is eliminated. Another major advantage of composite medical implants (eg, DiPhos-RM) is radiolucency, which allows direct visualization of osseous callus formation as well as monitoring of fracture healing, thereby improving clinical assessment and accuracy.