In the absence of adequate data on adult ADHD/BD, studies in children suggest:
- stimulants may not be effective for ADHD symptoms in patients with active manic or depressive symptoms
- mood stabilization is a prerequisite for successful pharmacologic treatment of ADHD in patients with both ADHD and manic or depressive symptoms.23,24
Follow the hierarchy. First treat acute mood symptoms, then reevaluate and possibly treat ADHD symptoms if they persist during euthymia (Algorithm 1). When a patient meets criteria for adult ADHD/BD, first stabilize bipolar manic or depressive symptoms (Algorithm 2). For acute mania, treat with standard mood stabilizers (lithium, valproate, lamotrigine, or carbamazepine) with or without a second-generation antipsychotic.25 Starting stimulants for ADHD when patients have active mood symptoms is sub-optimal and potentially harmful because of the risk of inducing mania. For acute bipolar depression, adjunctive antidepressant treatment has been found to be no more effective than a mood stabilizer alone.26
After bipolar symptoms respond or remit, reassess for adult ADHD. If ADHD symptoms persist during euthymia, additional treatment may be indicated.
Very little evidence exists on treating adult ADHD/BD; as mentioned, bupropion is the only medication studied in this population. For adult ADHD alone, clinical trials have showed varying efficacy with bupropion,27,28 atomoxetine,29 venlafaxine,30,31 desipramine,32 methylphenidate,33 mixed amphetamine salts,34 and guanfacine.35 Whether these treatments can be generalized as safe and efficacious for comorbid adult ADHD/BD is unclear. Nonetheless, we suggest using bupropion first, followed by atomoxetine or guanfacine before you consider amphetamine stimulants (Algorithm 3).
Algorithm 1
Hierarchy for diagnosis and treatment of adult ADHD/BD
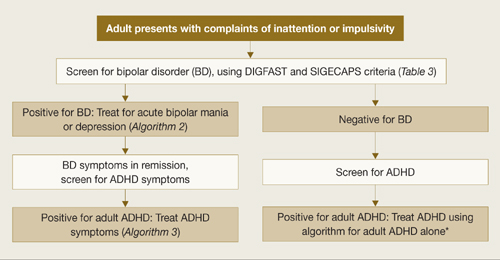
ADHD: attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder; BD: bipolar disorder
*Adler LA, Chua HC. Management of ADHD in adults. J Clin Psychiatry 2002;63(suppl 12):29-35.
Algorithm 2
Treating acute episodes of bipolar disorder
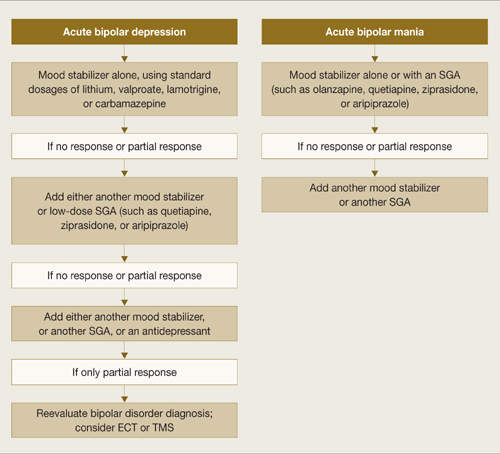
ECT: electroconvulsive therapy; SGA: second-generation antipsychotic; TMS: transcranial magnetic stimulation
Algorithm 3
Suggested approach to adult ADHD with comorbid BD*
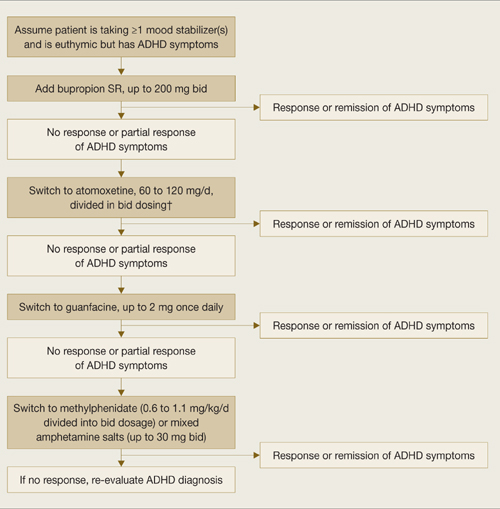
* Based on data extrapolated from samples of patients with ADHD alone because of very limited data in ADHD/BD samples.
† We recommend against combining antidepressants and stimulants because of additive risks of mania in BD. Discontinue stimulant or antidepressant if manic symptoms appear or rapid cycling emerges.
Reducing mania risk
Antidepressants and stimulants may help adults with ADHD alone, but risks of mania and rapid cycling limit their use in adults with ADHD/BD.
Stimulants and mania. One study found a 17% manic switch rate when methylphenidate (≤10 mg bid) was given to 14 bipolar depressed adults (10 BD type I, 2 BD type II, and 2 with secondary mania) taking mood stabilizers.36 A chart review of 82 bipolar children not taking mood stabilizers found an 18% switch rate with methylphenidate or amphetamine.37 Another chart review of 80 children with BD type I found that past amphetamine treatment (but not history of ADHD diagnosis or antidepressant treatment) was associated with more severe bipolar illness.38
No studies have examined predictors of amphetamine-induced mania. In our clinical experience, triggers are similar to those that can cause antidepressant-induced mania, such as:
- recent manic episodes
- current rapid cycling
- past antidepressant-induced mania.
Antidepressants and mania. When 64 patients with acute bipolar depression received both antidepressants and mood stabilizers in a randomized, double-blind trial, switch rates into mania or hypomania were 10% for bupropion, 9% for sertraline, and 29% for venlafaxine.39 In a meta analysis of clinical trials using selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) or tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs), the manic switch rate was threefold higher with TCAs than SSRIs.40 Antidepressant use in bipolar patients was associated with rapid cycling in the only randomized study of this topic.41
Insufficient data exist to clarify whether mania induction with antidepressants is dose-dependent.42 Factors associated with antidepressant-induced mania include:
- previous antidepressant-induced mania
- family history of BD
- exposure to multiple antidepressant trials42
- history of substance abuse and/or dependence.43
Related resources
- Bipolar disorder information and resources. www.psycheducation.org.
- ADHD Information and resources. www.adhdnews.com.
- Phelps J. Why am I still depressed? Recognizing and managing the ups and downs of bipolar II and soft bipolar disorder. New York: McGraw-Hill; 2006.
Drug brand names
- Amphetamine/Dextroamphetamine • Adderall
- Aripiprazole • Abilify
- Atomoxetine • Strattera
- Bupropion • Wellbutrin
- Carbamazepine • Tegretol
- Desipramine • Norpramin
- Dextroamphetamine • Dexedrine
- Guanfacine • Tenex
- Lamotrigine • Lamictal
- Lithium • Eskalith, Lithobid
- Methylphenidate • Ritalin
- Quetiapine • Seroquel
- Sertraline • Zoloft
- Valproate • Depakote
- Venlafaxine • Effexor
- Ziprasidone • Geodon
Disclosures
Dr. Wingo reports no financial relationship with any company whose products are mentioned in this article or with manufacturers of competing products.

