Determining CYP2D6 phenotype
Risperidone and venlafaxine levels are useful tools for predicting CYP2D6 phenotype.3,8 When a risperidone level is ordered, the results include a risperidone level and a 9-hydroxyrisperidone level. The active metabolite of risperidone is 9-hydroxyrisperidone (paliperidone). The risperidone-to-9-hydroxyrisperidone (R-to-9-OHR) concentration ratio is an indicator of CYP2D6 phenotype.3 While considerable overlap may exist using R-to-9-OHR concentration ratios as a predictor of CYP2D6 phenotype, this provides a practical and economically viable option for guiding drug therapy and recommending CYP2D6 genetic testing. The median R-to-9-OHR concentration ratios with the 25th to 75th percentiles are listed below as indicators of CYP2D6 phenotypes9:
- Ultra-rapid metabolizer: 0.03 (0.02 to 0.06)
- Extensive metabolizer: 0.08 (0.04 to 0.17)
- Intermediate metabolizer: 0.56 (0.30 to 1.0)
- Poor metabolizer: 2.5 (1.8 to 4.1).
Although a R-to-9-OHR concentration ratio >1 generally indicates a poor metabolizer, it could also indicate the presence of a powerful CYP2D6 inhibitor.9
When a venlafaxine level is ordered, the results include a venlafaxine level and an O-desmethylvenlafaxine level. O-desmethylvenlafaxine (desvenlafaxine) is the active metabolite of venlafaxine. The O-desmethylvenlafaxine-to-venlafaxine concentration ratio is an indicator of CYP2D6 phenotype.8 In this instance, a ratio ≥1 indicates an extensive metabolizer, whereas <1 indicates a poor metabolizer.
CYP1A2
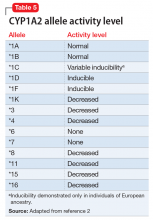
While the activity of CYP2D6 alleles is determined primarily by genetic factors and medications, the activity of CYP1A2 alleles is largely determined by environmental factors (diet, medications, disease) and genetic variability.2 Consequently, CYP1A2 genotyping may be less clinically useful than CYP2D6 genotyping. The CYP1A2 genotype–phenotype relationship incorporates the degree of allele activity (Table 52), and inducibility in the presence of environmental factors.
Continue to: CYP1A2 inhibiton