Surgeons as leaders
What do we know about surgeons as physician leaders? Looking at the previously mentioned lists of physician leaders, surgeons are relatively absent. In the Becker’s Hospital Review study of nonprofit hospitals, only 9% of CEOs were surgeons.10 In addition, when reviewing data that associated physician leaders and hospital performance, only 3 of the CEOs were surgeons.11 Given that surgeons make up approximately 19% of US physicians, we are underrepresented.
The omission of surgeons as leaders seems inappropriate given that most hospitals are financially reliant on revenue related to surgical care and optimizing this space is an enormous opportunity. Berger and colleagues offered 3 theories as to why there are fewer surgeon leaders16:
- The relative pay of surgeons exceeds that of most other specialties, and there may be less incentive to accept the challenges presented by leadership roles. (I will add that surgeon leadership is more costly to a system.)
- The craftsmanship nature of surgery discourages the development of other career interests beginning at the trainee level.
- Surgeons have been perceived stereotypically to exhibit arrogance, a characteristic that others may not warm to.
This last observation stings. Successful leadership takes social skill and teamwork.14 Although medical care is one of the few disciplines in which lack of teamwork might cost lives, physicians are not trained to be team players. We recognize how our training has led us to be lone wolves or gunners, situations where we as individuals had to beat others to secure our spot. We have been trained in command-and-control environments, in stepping up as a leader in highly stressful situations. This part of surgical culture may handicap surgeons in their quest to be health care leaders.
Other traits, however, make us particularly great leaders in health care. Our desire to succeed, willingness to push ourselves to extremes, ability to laser focus on a task, acceptance of delayed gratification, and aptitude for making timely decisions on limited data help us succeed in leadership roles. Seven years of surgical training helped me develop the grit I use every day in the C-suite.
We need more physician and surgeon leadership to thrive in the challenging health care landscape. Berger and colleagues proposed 3 potential solutions to increase the number of surgeons in hospital leadership positions16:
Nurture future surgical leaders through exposure to management training. Given the contribution to both expense in support services and resources and revenue related to surgical care, each organization needs a content expert to guide these decisions.
Recognize the important contributions that surgeons already make regarding quality, safety, and operational efficiency. An excellent example of this is the American College of Surgeons National Surgical Quality Improvement Program. Because surgeons are content experts in this area, we are primed to lead.
Hospitals, medical schools, and academic departments of surgery should recognize administrative efforts as an important part of the overall academic mission. As the adage states, “No margin, no mission.” We need bright minds to preserve and grow our margins so that we can further invest in our missions.
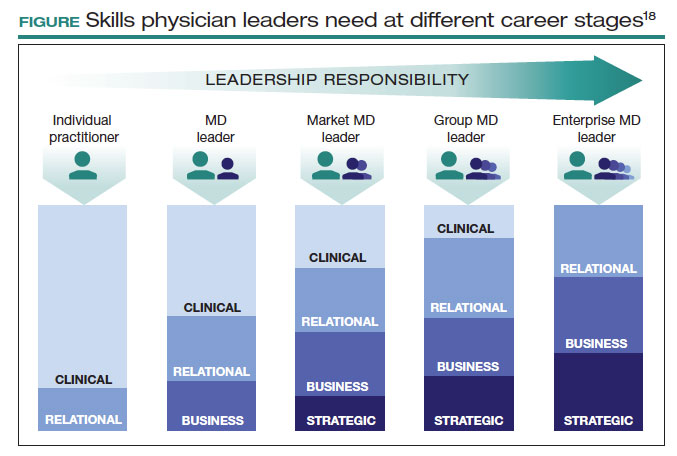
This is not easy. Given the barriers, this will not happen organically. Charan and colleagues provided an outline for a leadership pathway adapted for physicians (FIGURE).17,18 It starts with the individual practitioner who is a practicing physician and spends most of their time focused on patient care. As a physician becomes more interested in leadership, they develop new skills and take on more and more responsibility. As they increase in leadership responsibility, they tend to reduce clinical time and increase time spent on strategic and business management. This framework creates a pipeline so that physicians and surgeons can be developed strategically and given increasing responsibility as they develop their capabilities and expand their skill sets.
The leadership challenge
To thrive, we must transform health care by changing how we practice medicine. As ObGyns, we are the leaders we have been waiting for. As you ponder your future, think of your current career and the opportunities you might have. Do you have a seat at the table? What table is that? How are you using your knowledge, expertise, and privilege to advance health care and medicine? I challenge you to critically evaluate this—and lead. ●