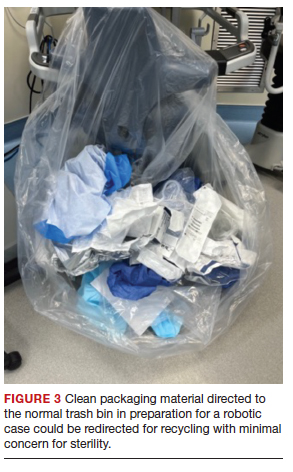
Packaging material
A substantial part of OR waste consists of packaging material; of all OR waste, 26% consists of plastics and 7%, paper and cartons.14 Increasing use of disposable or “single use” medical products in ORs, along with the intention to safeguard sterility, contributes significantly to the generation of medical waste in operating units. Containers, wraps and overwraps, cardboard, and plastic packaging are all composed of materials that when clean, can be recycled; however, these items often end up in the landfill (FIGURE 3).
Although the segregation of packaging material to recycling versus regular trash versus red bin is of paramount importance, packaging design plays a significant role as well. In 2018, Boston Scientific introduced a new packaging design for ureteral stents that reduced plastic use in packaging by 120,000 lb each year.15 Despite the advances in the medical packaging industry to increase sustainability while safeguarding sterility for medical devices, there is still room for innovation in this area.
Reducing overage by judicious selection of surgical devices, instruments, and supplies
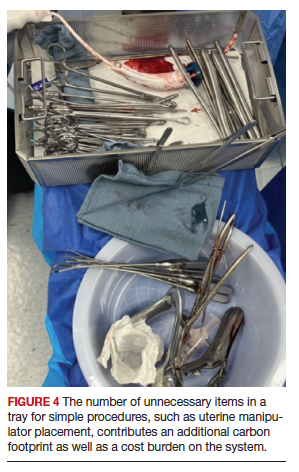
Overage is the term used to describe surgical inventory that is opened and prepared for surgery but ultimately not used and therefore discarded. Design of surgical carts and instrument and supply selection requires direct input from ObGyns. Opening only the needed instruments while ensuring ready availability of potentially needed supplies can significantly reduce OR waste generation as well as decrease chemical pollution generated by instrument sterilization. Decreasing OR overage reduces overall costs as well (FIGURE 4).
In a pilot study at the University of Massachusetts, Albert and colleagues examined the sets of disposable items and instruments designated for common plastic and hand surgery procedures.11 They identified the supplies and instruments that are routinely opened and wasted, based on surgeons’ interview responses, and redesigned the sets. Fifteen items were removed from disposable plastic surgery packs and 7 items from hand surgery packs. The authors reported saving thousands of dollars per year with these changes alone, as well as reducing waste.11 This same concept easily could be implemented in obstetrics and gynecology. We must ask ourselves: Do we always need, for example, a complete dilation and curettage kit to place the uterine manipulator prior to a minimally invasive hysterectomy?
In another pilot study, Greenberg and colleagues investigated whether cesarean deliveries consistently could be performed in a safe manner with only 20 instruments in the surgical kit.16 Obstetricians rated the 20-instrument kit an 8.7 out of 10 for performing cesarean deliveries safely.16
In addition to instrument selection, surgeons have a role in other supply use and waste generation: for instance, opening multiple pairs of surgical gloves and surgical gowns in advance when most of them will not be used during the case. Furthermore, many ObGyn surgeons routinely change gloves or even gowns during gynecologic procedures when they go back and forth between the vaginal and abdominal fields. Is the perineum “dirty” after application of a surgical prep solution?
In an observational study, Shockley and colleagues investigated the type and quantity of bacteria found intraoperatively on the abdomen, vagina, surgical gloves, instrument tips, and uterus at distinct time points during total laparoscopic hysterectomy.17 They showed that in 98.9% of cultures, the overall bacterial concentrations did not exceed the threshold for infection. There was no bacterial growth from vaginal cultures, and the only samples with some bacterial growth belonged to the surgeon’s gloves after specimen extraction; about one-third of samples showed growth after specimen extraction, but only 1 sample had a bacterial load above the infectious threshold of 5,000 colony-forming units per mL. The authors therefore suggested that if a surgeon changes gloves, doing so after specimen extraction and before turning attention back to the abdomen for vaginal cuff closure may be most effective in reducing bacterial load.17
Surgical site infection contributes to medical cost and likely medical waste as well. For example, surgical site infection may require prolonged treatments, tests, and medical instruments. In severe cases with abscesses, treatment entails hospitalization with prolonged antibiotic therapy with or without procedures to drain the collections. Further research therefore is warranted to investigate safe and environmentally friendly practices.
Myriad products are introduced to the medical system each day, some of which replace conventional tools. For instance, low-density polyethylene, or LDPE, transfer sheet is advertised for lateral patient transfer from the OR table to the bed or stretcher. This No. 4–coded plastic, while recyclable, is routinely discarded as trash in ORs. One ergonomic study found that reusable slide boards are as effective for reducing friction and staff muscle activities and are noninferior to the plastic sheets.18
Steps to making an impact
Operating rooms and labor and delivery units are responsible for a large proportion of hospital waste, and therefore they are of paramount importance in reducing waste and carbon footprint at the individual and institutional level. Reduction of OR waste not only is environmentally conscious but also decreases cost. Steps as small as individual practices to as big as changing infrastructures can make an impact. For instance:
- redesigning surgical carts
- reformulating surgeon-specific supply lists
- raising awareness about surgical overage
- encouraging recycling through education and audit
- optimizing surgical waste segregation through educational posters.
These are all simple steps that could significantly reduce waste and carbon footprint.
Bottom line
Although waste reduction is the responsibility of all health care providers, as leaders in their workplace physicians can serve as role models by implementing “green” practices in procedural units. Raising awareness and using a team approach is critical to succeed in our endeavors to move toward an environmentally friendly future. ●