An alternative to Foley use if a patient does not know CISC
Boyd SS, O'Sullivan DM, Tunitsky-Bitton E. A comparison of two methods of catheter management after pelvic reconstructive surgery: a randomized controlled trial. Obstet Gynecol. 2019;134:1037-1045.
The traditional indwelling catheter as a postoperative bladder drainage method has a number of drawbacks, including an increased rate of UTI, patient discomfort, and potential limitations in mobility due to the presence of a drainage bag.5
Boyd and colleagues reported on a variation of traditional transurethral catheterization that hypothetically allows for improved mobility. With this method, the transurethral catheter is occluded with a plastic plug that is intermittently plugged and unplugged (plug-unplug method) for bladder drainage. To test whether activity levels are improved with the plug-unplug method versus the continuous drainage approach, the authors conducted an RCT in women undergoing pelvic reconstructive surgery to compare the plug-unplug method with transurethral catheterization (with a continuous drainage bag) and a reference group of freely voiding women.
Study particulars and outcomes
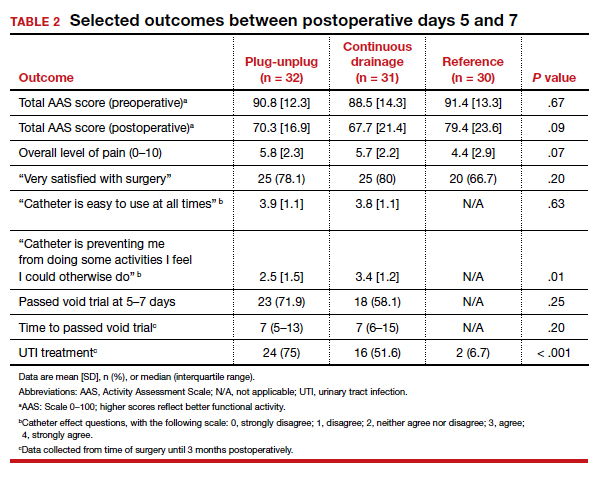
The trial's primary outcome was the patients' activity score as measured by the Activity Assessment Scale (AAS) at 5 to 7 days postoperatively. Because of the theoretically increased risk of a UTI with opening and closing a closed drainage system, secondary outcomes included the UTI rate, the time to pass an outpatient void trial, postoperative pain, patient satisfaction, and catheter effect. To detect an effect size of 0.33 in the primary outcome between the 3 groups, 90 participants were needed along with a difference in proportions of 0.3 between the catheterized and noncatheterized groups.
The participants were randomly assigned 1:1 preoperatively to the continuous drainage or plug-unplug method. All patients underwent a backfill-assisted void trial prior to hospital discharge; the first 30 randomly assigned patients to pass their void trial comprised the reference group. Patients in the plug-unplug arm were instructed to uncap the plastic plug to drain their bladder when they felt the urge to void or at least every 4 hours. All catheterized patients were provided with a large drainage bag for gravity-based drainage for overnight use.
Participants who were discharged home with a catheter underwent an outpatient void trial between postoperative days 5 and 7. A urinalysis was performed at that time and a urine culture was done if a patient reported UTI symptoms. All patients underwent routine follow-up until they passed the office void trial.
Results. Ninety-three women were included in the primary analysis. There were no differences in baseline characteristics between groups. No difference was detected in activity by AAS scores between all 3 groups (scores: plug-unplug, 70.3; continuous drainage, 67.7; reference arm, 79.4; P = .09). The 2 treatment arms had no overall difference in culture-positive UTI (plug-unplug, 68.8%; continuous drainage, 48.4%; P = .625). No significant difference was found in the percentage of patients who passed their initial outpatient void trial (plug-unplug, 71.9%, vs continuous drainage, 58.1%; P = .25) (TABLE 2).
Catheter impact on postoperative activity considered
Strengths of the study include the prospective randomized design, the inclusion of a noncatheterized reference arm, and use of a validated questionnaire to assess activity. The study was limited, however, by the inability to blind patients to treatment and the lack of power to assess other important outcomes, such as UTI rates.
Although the authors did not find a difference in activity scores between the 2 catheterization methods, no significant difference was found between the catheterized and noncatheterized groups, which suggests that catheters in general may not significantly impact postoperative activity. The theoretical concern that opening and closing a transurethral drainage system would increase UTI rates was not substantiated, although the study was not powered specifically for this outcome.
Ultimately, the plug-unplug method may be a safe alternative for patients who desire to avoid attachment to a drainage bag postoperatively.
Based on the results of an RCT that compared 2 methods of catheter management after pelvic reconstructive surgery, the plug-unplug catheterization method may be an acceptable alternative to traditional catheterization.
- Bladder backfill in the operating room followed by spontaneous void in the postanesthesia care unit (PACU) is a safe and efficient way to assess for postoperative voiding dysfunction.
- Voids of 200 mL or more (following a 300-mL backfill) may not require a PACU postvoid residual assessment.
- Postoperative activity does not appear to be impacted by the presence of an indwelling catheter.
Continue to: Does antibiotic prophylaxis reduce UTI for patients catheter-managed postoperatively?