Hysteroscopy and endometrial carcinoma
The most common type of gynecologic cancer in the United States is endometrial adenocarcinoma (type 1 endometrial cancer). There is some concern about the effect of hysteroscopy on endometrial cancer prognosis and the spread of cells to the peritoneum at the time of hysteroscopy. A large meta-analysis found that hysteroscopy performed in the presence of type 1 endometrial cancer statistically significantly increased the likelihood of positive intraperitoneal cytology; however, it did not alter the clinical outcome. It was recommended that hysteroscopy not be avoided for this reason and is helpful in the diagnosis of endometrial cancer, especially in the early stages of disease.8
For endometrial cancer type 2 (serous carcinoma, clear cell carcinoma, and carcinosarcoma), Chen and colleagues reported a statistically significant increase in positive peritoneal cytology for cancers evaluated by hysteroscopy versus D&C. The disease-specific survival for the hysteroscopy group was 60 months, compared with 71 months for the D&C group. While this finding was not statistically significant, it was clinically relevant, and the effect of hysteroscopy on prognosis with type 2 endometrial cancer is unclear.9
A common occurrence in the evaluation of postmenopausal bleeding (PMB) is an initial TVUS finding of an enlarged endometrium and an endometrial biopsy that is negative or reveals scant or insufficient tissue. Unfortunately, the diagnostic evaluation process often stops here, and a diagnosis for the PMB is never actually identified. Here are several clinical scenarios that highlight the need for hysteroscopy in the initial evaluation of PMB, especially when there is a discordance between transvaginal ultrasonography (TVUS) and endometrial biopsy findings.
Patient 1: Discordant TVUS and biopsy, with benign findings
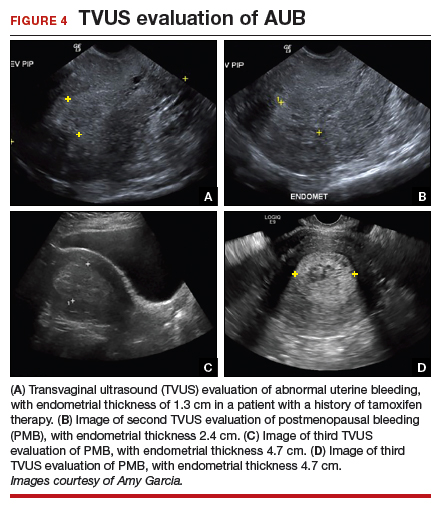
The patient is a 52-year-old woman who presented to her gynecologist reporting abnormal uterine bleeding (AUB). She has a history of breast cancer, and she completed tamoxifen treatment. Pelvic ultrasonography was performed; an enlarged endometrial stripe of 1.3 cm was found (FIGURE 4A). Endometrial biopsy was performed, showing adequate tissue but with a negative result. The patient is told that she is likely perimenopausal, which is the reason for her bleeding.
At the time of referral, the patient is evaluated with in-office hysteroscopy. Diagnosis of a 5 cm x 7 cm benign endometrial polyp is made. An uneventful hysteroscopic polypectomy is performed (VIDEO 2).
Video 2

This scenario illustrates the shortcoming of initial evaluation by not performing a hysteroscopy, especially in a woman with a thickened endometrium with previous tamoxifen therapy. Subsequent visits failed to correlate bleeding etiology with discordant TVUS and endometrial biopsy results with hysteroscopy, and no hysteroscopy was performed in the operating room at the time of D&C.
Patient 2: Discordant TVUS and biopsy, with premalignant findings
The patient is a 62-year-old woman who had incidental findings of a thickened endometrium on computed tomography scan of the pelvis. TVUS confirmed a thickened endometrium measuring 17 mm, and an endometrial biopsy showed scant tissue.
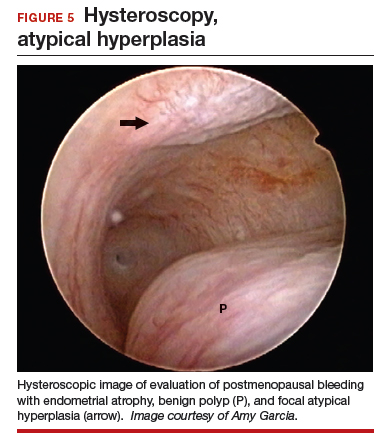
At the time of referral, a diagnostic hysteroscopy was performed in the office. Endometrial atrophy, a large benign appearing polyp, and focal abnormal appearing tissue were seen (FIGURE 5). A decision for polypectomy and directed biopsy was made. Histology findings confirmed benign polyp and atypical hyperplasia (VIDEO 3).
Video 3

This scenario illustrates that while the patient was asymptomatic, there was discordance between the TVUS and endometrial biopsy. Hysteroscopy identified a benign endometrial polyp, which is common in asymptomatic postmenopausal patients with a thickened endometrium and endometrial biopsy showing scant tissue. However, addition of the diagnostic hysteroscopy identified focal precancerous tissue, removed under directed biopsy.
Patient 3: Discordant TVUS and biopsy, with malignant findings
The patient is a 68-year-old woman with PMB. TVUS showed a thickened endometrium measuring 14 mm. An endometrial biopsy was negative, showing scant tissue. No additional diagnostic evaluation or management was offered.
Video 4A

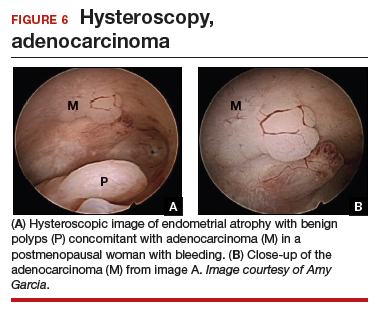
At the time of referral, the patient was evaluated with in-office diagnostic hysteroscopy, and the patient was found to have endometrial atrophy, benign appearing polyps, and focal abnormal tissue (FIGURE 6). A decision for polypectomy and directed biopsy was made. Histology confirmed benign polyps and grade 1 adenocarcinoma (VIDEOS 4A, 4B, 4C).
Video 4B

This scenario illustrates the possibility of having multiple endometrial pathologies present at the time of discordant TVUS and endometrial biopsy. Hysteroscopy plays a critical role in additional evaluation and diagnosis of endometrial carcinoma with directed biopsy, especially in a symptomatic woman with PMB.
Video 4C