The results were collated using descriptive statistics. The χ2 test was used to compare categorical data between those patients who were and were not reviewed by a neurologist, and the Mann-Whitney U test was used to compare differences in the length of stay between these 2 groups.
No national data relating to this specific patient group were available within the literature. Therefore, to provide a comparator of neurological patients within the same hospital, data were collected on stroke patients managed on the stroke ward. This group was deemed most appropriate for comparison as they present with similar neurological symptoms but are cared for on a specialist ward. During the evaluation period, 284 stroke patients were admitted to the stroke ward. A sample of 75 patients was randomly selected using a random number generator, and the procedure for data collection was repeated. It was not appropriate to make direct comparative analysis on these 2 groups due to the inherent differences, but it was felt important to provide context with regards to what usual care was like on a specialist ward within the same hospital.
Ethical approval was not required as this was a service evaluation of routinely collected data within a single hospital site.
Results
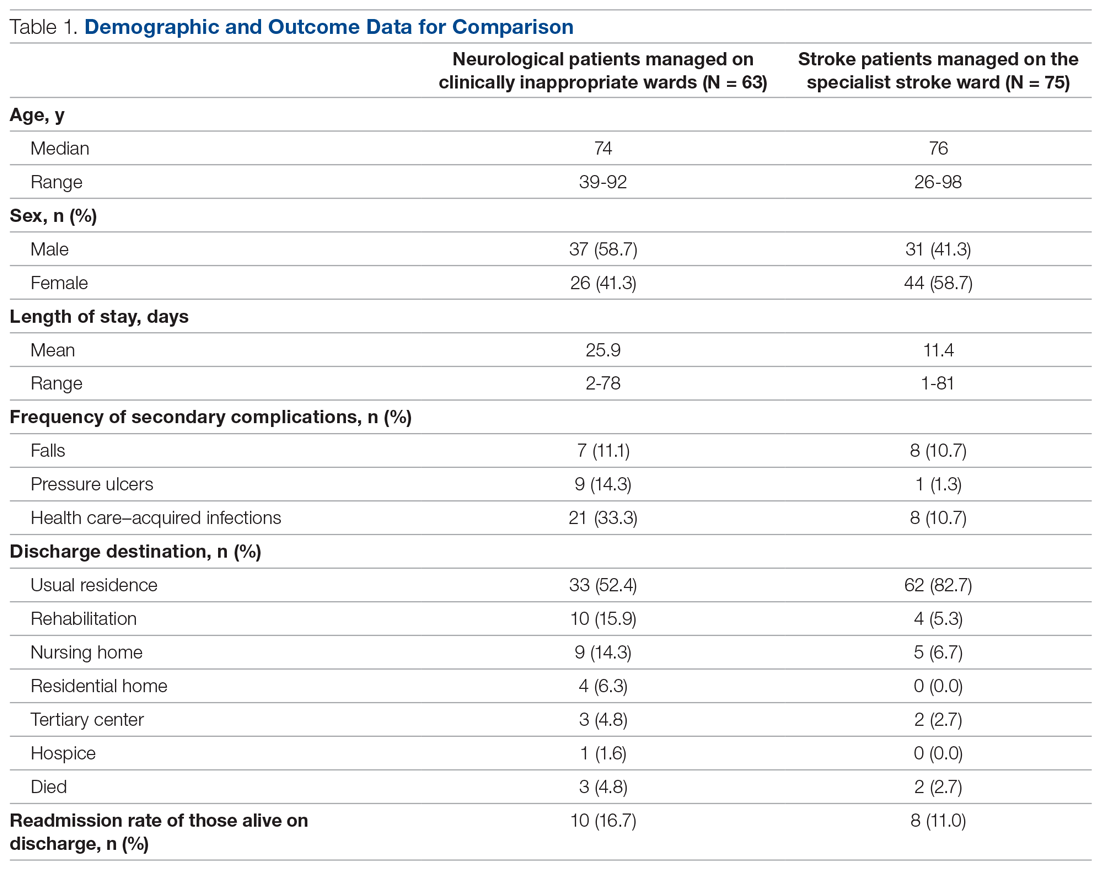
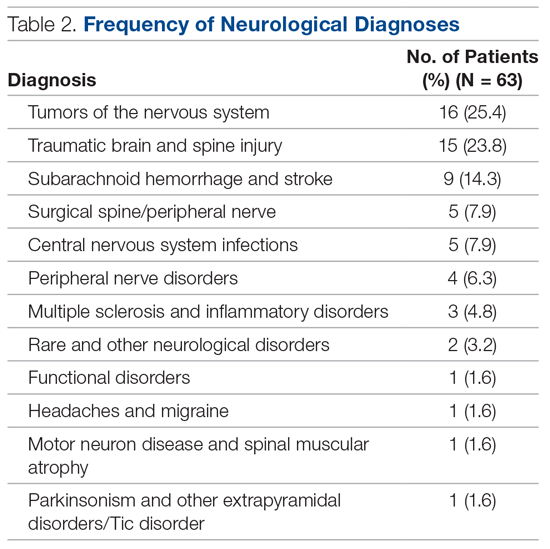
In total, 63 patients were identified: 26 females and 37 males. The median age of patients was 74 years (range, 39-92 years). These demographic details and comparisons to stroke patients managed on a specialist ward can be seen in Table 1. To quantify the range of diagnoses, the condition groups defined by GIRFT Neurology Methodology9 were used. The most common diagnoses were tumors of the nervous system (25.4%) and traumatic brain and spine injury (23.8%). The other conditions included in the analysis can be seen in Table 2.
Despite having a neurological condition as their primary diagnosis, only 15.9% of patients were reviewed by a neurologist during their hospital admission. Patients were most commonly under the care of a geriatrician (60.3%), but they were also managed by orthopedics (12.6%), acute medicine (7.9%), respiratory (6.3%), cardiology (4.8%), gastroenterology (3.2%), and surgery (3.2%). One patient (1.6%) was managed by intensivists.