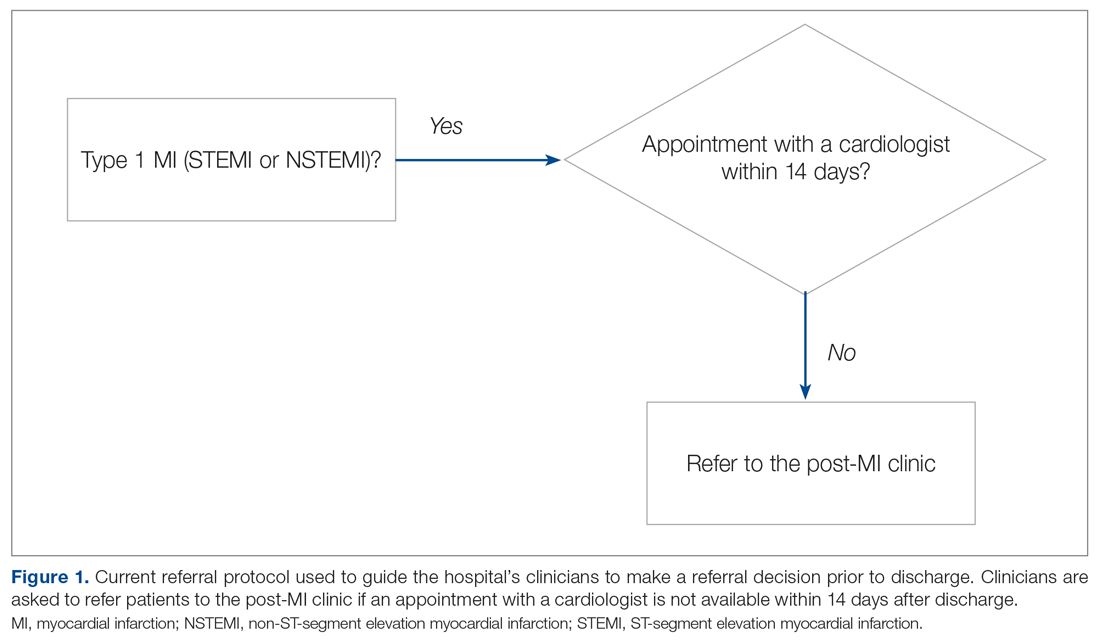
Our hospital’s postmyocardial infarction clinic was created to prevent unplanned readmissions within 30 days after discharge among patients with type I myocardial infarction (MI). Since inception, the number of referrals has been much lower than expected. In 2018, the total number of patients discharged from the hospital with type I MI and any troponin I level above 0.40 ng/mL was 313. Most of these patients were discharged from the hospital’s cardiac units; however, only 91 referrals were made. To increase referrals, the cardiology nurse practitioners (NPs) developed a post-MI referral protocol (Figure 1). However, this protocol was not consistently used and referrals to the clinic remained low.
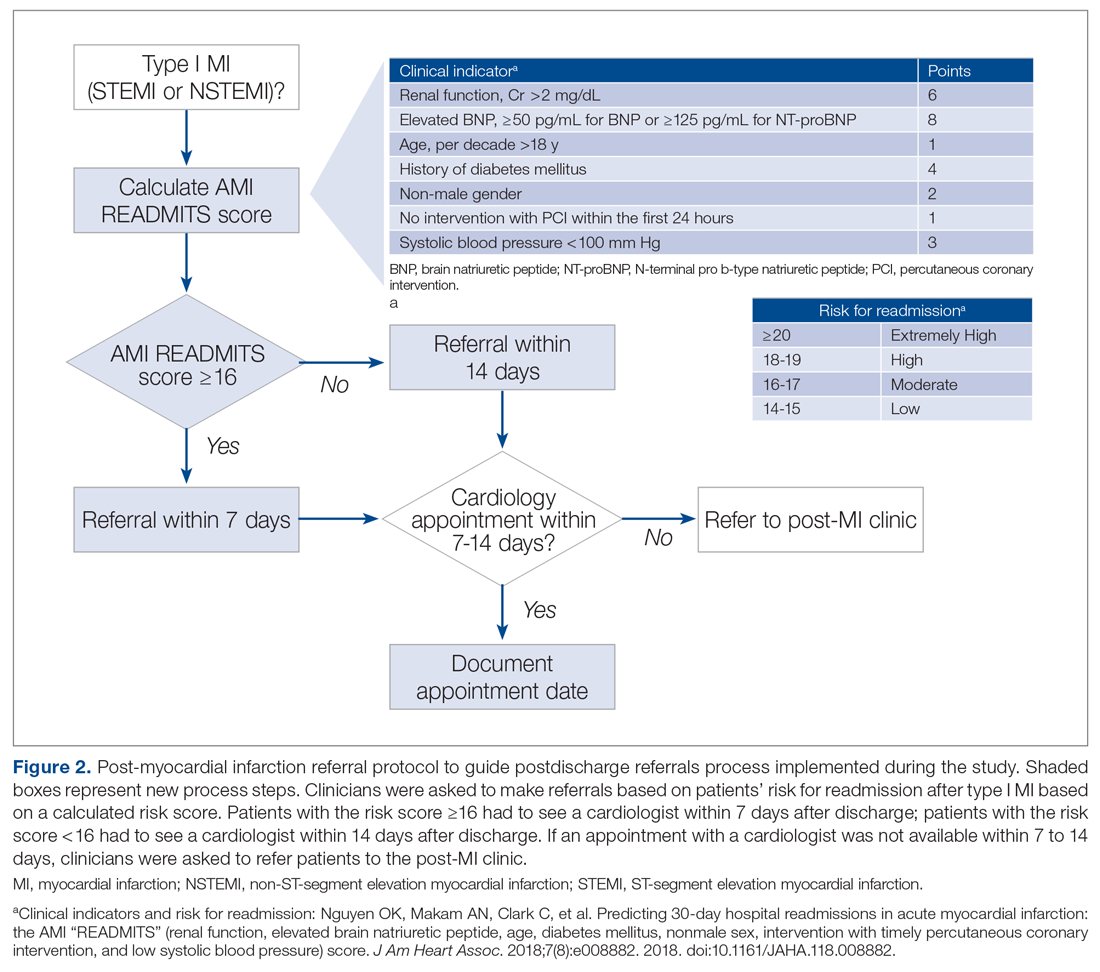
Evidence-based risk assessment tools have the potential to increase effective patient management. For example, cardiology providers at the hospital utilize various scores, such as CHA2DS2-VASc6 and the Society of Thoracic Surgery risk score,7 to plan patient management. Among the scores used to predict unplanned readmissions for MI patients, the most promising is the AMI READMITS score.8 Unlike other nonspecific prediction models, the AMI READMITS score was developed based on variables extracted from the electronic health records (EHRs) of patients who were hospitalized for MI and readmitted within 30 days after discharge. Recognizing the potential to increase referrals by integrating an MI-specific risk assessment, this quality improvement study modified the existing referral protocol to include the patients’ AMI READMITS score and recommendations for follow-up.
Currently, there are no clear recommendations on how soon after discharge patients with MI should undergo follow-up. As research data vary, we selected 7 days follow-up for patients from high risk groups based on the “See you in 7” initiative for patients with heart failure (HF) and MI,9,10 as well as evidence that patients with NSTEMI have a lower risk of 30-day readmission if they have follow-up within 7 days after discharge5; and we selected 14 days follow-up for patients from low-risk groups based on evidence that postdischarge follow-up within 14 days reduces risk of 30-day readmission in patients with acute myocardial infarction (AMI) and/or acutely decompensated HF.11
Methods
This project was designed to answer the following question: For adult patients with type I MI, does implementation of a readmission risk assessment referral protocol increase the percentage of referrals and appointments scheduled within a recommended time? Anticipated outcomes included: (1) increased referrals to a cardiologist or the post-MI clinic; (2) increased scheduled follow-up appointments within 7 to 14 days; (3) provider satisfaction with the usability and usefulness of the new protocol; and (4) consistent provider adoption of the new risk assessment referral protocol.
To evaluate the degree to which these outcomes were achieved, we reviewed patient charts for 2 months prior and 2 months during implementation of the new referral protocol. As shown in Figure 2, the new protocol added the following process steps to the existing protocol: calculation of the AMI READMITS score, recommendations for follow-up based on patients’ risk score, and guidance to refer patients to the post-MI clinic if patients did not have an appointment with a cardiologist within 7 to 14 days after discharge. Patients’ risk assessment scores were obtained from forms completed by clinicians during the intervention. Clinician’s perceptions related to the usability and usefulness of the new protocol and feedback related to its long-term adoption were assessed using a descriptive survey.