Results
There were a total of 44 subjects recruited for the study. One intervention subject and one control subject were lost to follow-up, leaving 42 subjects who completed the study exit visit.
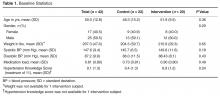
Baseline Statistics
Table 1 presents the baseline statistics for the subjects. There were no statistical differences in demographics, baseline biometrics, medication load, and hypertension knowledge between the control and intervention group.
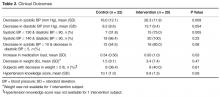
Clinical Outcomes
Table 2 presents the clinical outcomes of the study. Inter-vention subjects achieved a statistically greater decrease in systolic blood pressure than controls. There was also a strong trend toward a greater decrease in diastolic blood pressure. Statistically more intervention subjects than control subjects achieved a goal blood pressure ≤ 130/80 mm Hg. Fully 100% of intervention subjects achieved a goal blood pressure ≤ 140/90 mm Hg. This was not significantly more than control subjects. More intervention subjects had a decrease in blood pressure ≥ 10 mm Hg systolic and ≥ 5 mm Hg diastolic, but this result was not statistically significant. Intervention subjects had a greater increase in medication load than control subjects, but the average increase in medication load was less than 1. Changes in weight were not statistically significant, nor were changes in hypertension knowledge.
Cost
Table 3 presents a summary of nurse coach communications with subjects and the corresponding cost. The coach communicated with intervention subjects primarily through instant messages using the CollaboRhythm tablet application. There were trends toward more e-mails, phone calls, and office visits in control subjects that were not statistically significant. The total nurse coach time spent per patient was calculated using the following assumptions: instant message = 5 minutes, e-mail = 10 minutes, phone call = 15 minutes, office visit = 30 minutes. It is of note that, although virtual visits (video conferences with the ability to co-navigate patient data) were available as a feature, none were conducted during the course of the study. There was a trend toward intervention subjects receiving more support from the nurse coach that was not statistically significant. The cost associated with nurse coach time was calculated for both control and intervention subjects using the assumption of $50/hour (based on $100,000/year average salary plus benefits for nurse with health coaching certification). On average, intervention subjects received 0.28 hours or 16.8 minutes more time at an additional cost of $14.09.
Experience
Thirteen control subjects and 16 intervention subjects provided an experience rating during their exit interview from the study. There was a trend toward greater satisfaction by intervention subjects that was not statistically significant (8.9 vs. 7.6, P = 0.12). The majority of feedback from intervention subjects was obtained through the exit interview. The feedback was overwhelmingly positive. All of the subjects wanted to continue using the CollaboRhythm application after the end of the study. Some who had reached goal only wanted to use it sporadically as a “check-in,” but the majority wanted to use it daily as they had for the study for an indefinite period of time. They felt that the burden of reporting was easily balanced by the value of being able to track progress and get the efficient support of a health coach. They related that awareness of the associations between actions (diet, exercise, stress management, medication adherence) and blood pressure outcomes was integral to their success and their positive experience with the application. Subjects responded very favorably to the concept of leading their care. Some comments from patients include: “It felt good to take responsibility,” “No one has ever asked me to take responsibility for my health,” and “I developed confidence that I never would have had.” The nurse coach commented multiple times how delighted she was with the level of patient engagement and excitement. She also did not want to stop using the application at the end of the study.