Pulmonary Hypertension: Comorbidities and Novel Therapeutics
Mary Jo S. Farmer, MD, PhD
Associate Professor
Department of Medicine
UMASS CHAN Medical School
Worcester, MA
Physician
Pulmonary & Critical Care Division
Baystate Health
Springfield, MA
Mary Jo S. Farmer, MD, PhD, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.

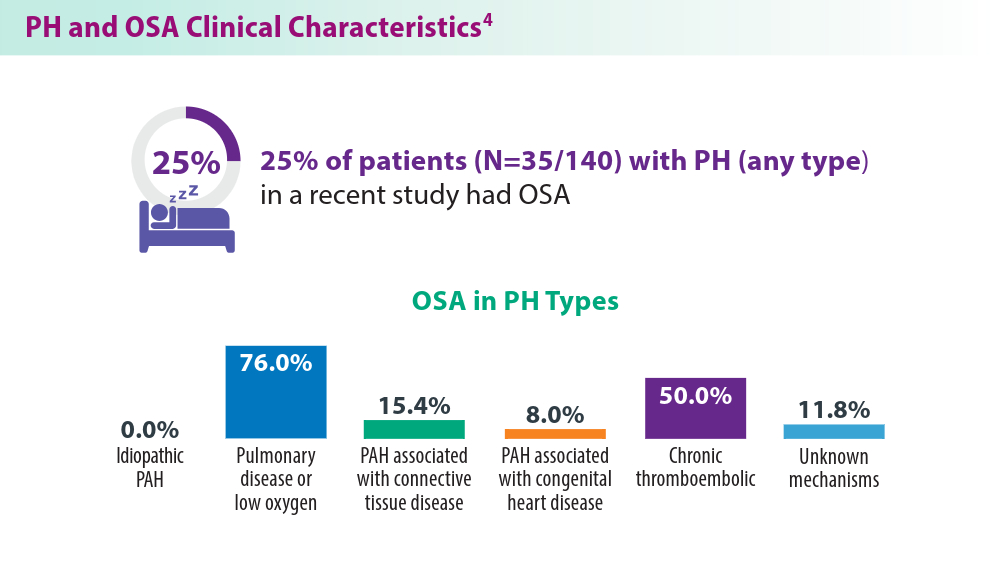
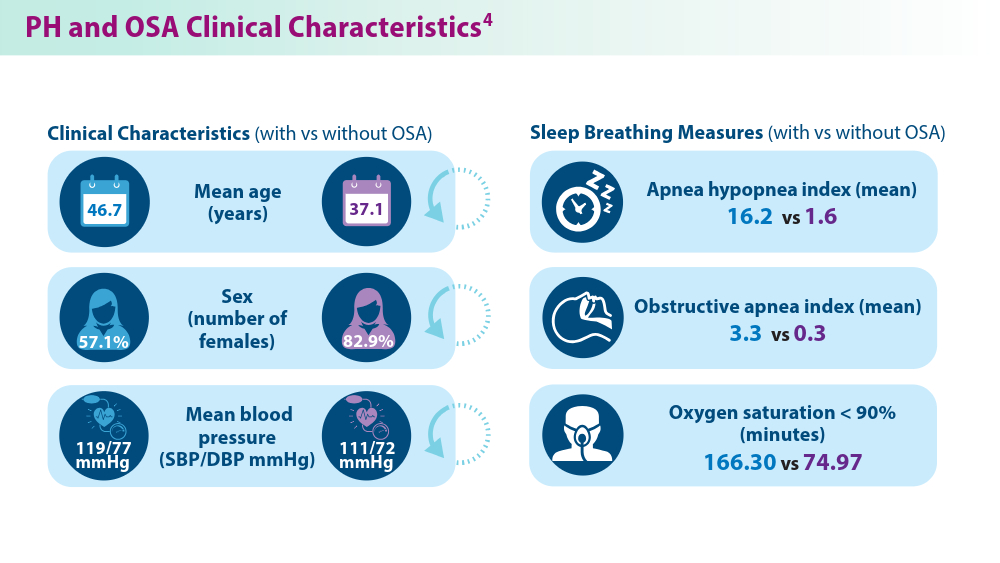
Pulmonary hypertension (PH), a disease of the pulmonary vasculature characterized by mean arterial pressure of > 20 mmHg, has high mortality and morbidity and encompasses a series of conditions.1,2 The 5 groups of PH as defined by WHO include pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH; group 1), pulmonary hypertension with left-sided heart disease (PH-LHD; group 2), PH with chronic lung disease (group 3), PH associated with blood clots and scarring as a complication of long-term pulmonary embolism or thromboembolic disease (CTEPH; group 4), and multifactorial or unclear mechanism PH (group 5).2 Many comorbidities predispose patients to PH and interact with disease features, such as congenital heart disease, chronic lung disease, interstitial lung disease, COPD, endemic infections, systemic hypertension, diabetes, coronary artery disease, and sleep apnea.2,3 For example, features of sleep apnea interact with PH, changing clinical sleep breathing measures.4
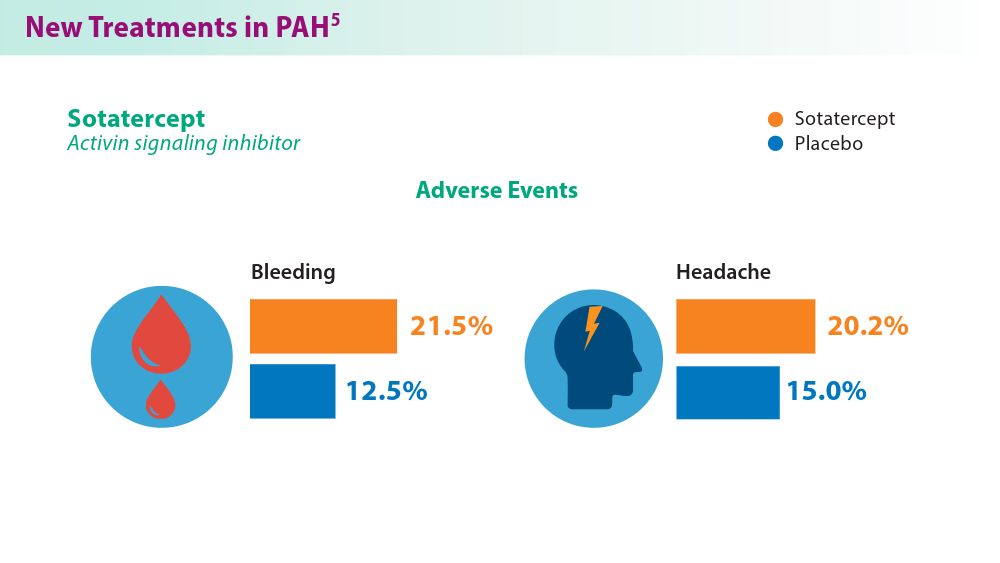
Efforts in recent years have focused on improving disease management and developing treatment options that target novel pathways, especially so in PAH.1,5,6 A recently approved treatment, sotatercept, is a novel fusion protein that attempts to restore balance between growth-promoting and growth-inhibiting signaling pathways in PAH. Sotatercept has been shown to improve 6-minute walk distance, a measure of aerobic capacity.5 Established PAH oral therapies are now available in single-tablet combinations (macitentan/tadalafil), which have demonstrated improvements in pulmonary vascular resistance compared with either medicine alone.6 For chronic thromboembolic disease, treatment approaches such as balloon pulmonary angioplasty are being used to improve cardiopulmonary outcomes and are constantly advancing.7 These new treatments provide additional options in management of the various manifestations of this chronic disease.
1
-
-
-
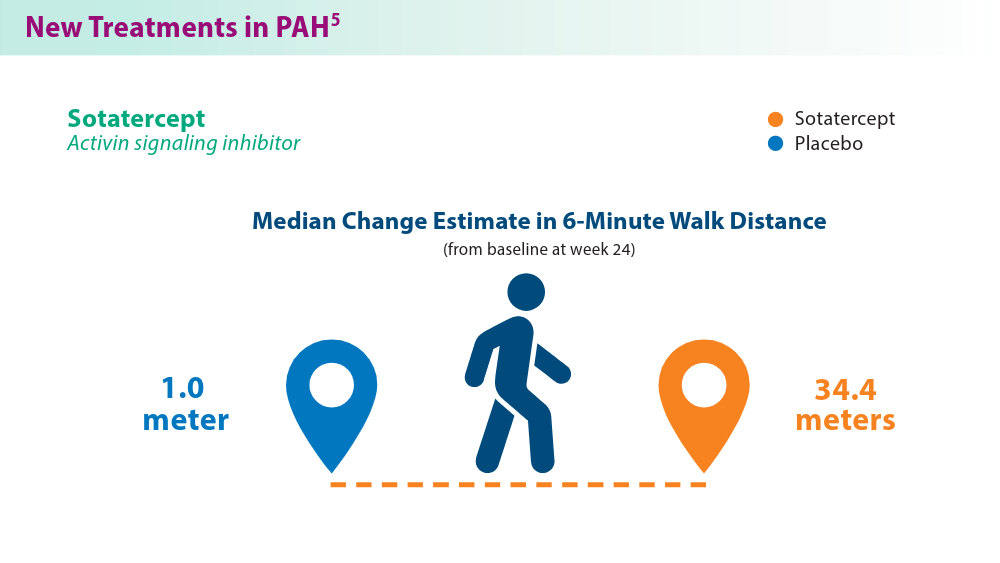
All patients received stable background therapy before and during treatment.
-
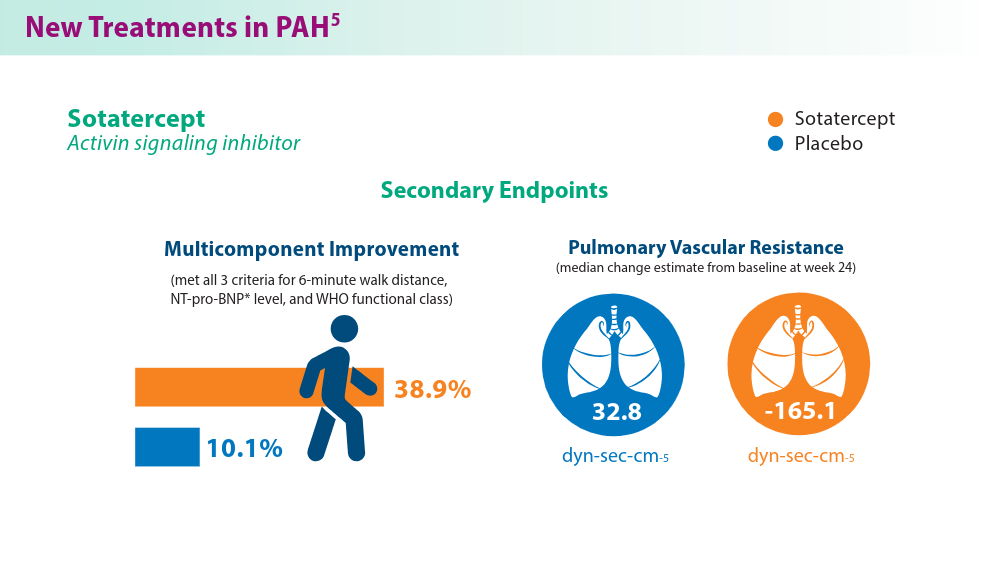
*NT-pro-BNP, N-terminal pro b-type natriuretic peptide
-
-
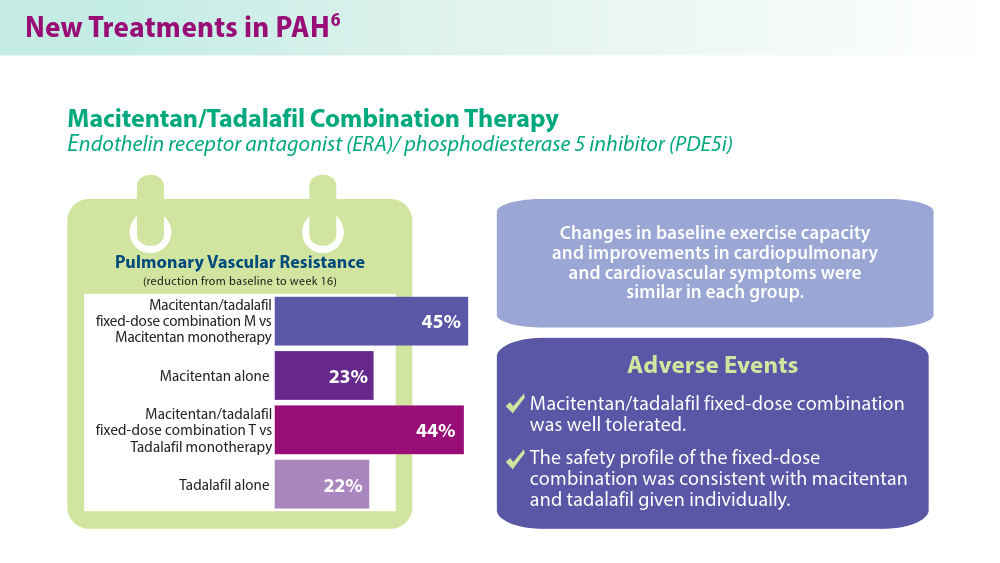
Macitentan/tadalafil M fixed-dose combination refers to patients who were treatment-naïve or on prior ERA at baseline. Macitentan/tadalafil T fixed-dose combination refers to patients who were treatment-naïve or on prior PDE5i at baseline.
