New anticancer drugs are often expensive and have been accompanied by large increases in the cost of medical treatment, but they also are associated with gains in life expectancy, according to an analysis of Medicare data published online.
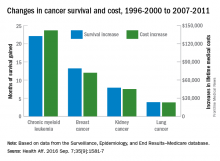
Investigators looked at four different types of cancer – breast, kidney, lung, and chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) – over two time periods: 1996-2000 and 2007-2011. Patients treated for CML during 2007-2011 had the largest increases in both average lifetime medical cost ($142,000) and months of life gained (22.1) over those treated during 1996-2000, reported David H. Howard, PhD, of Emory University, Atlanta, and his associates.
Breast cancer patients had the next-largest increases: 13.2 months of life expectancy and $72,000 in lifetime medical cost for those who received physician-administered intravenous drugs. For breast cancer patients who received only oral drugs, the increases were 2 months of life and $9,000 in lifetime cost, they noted.
Patients with kidney cancer had an average life-expectancy increase of 7.9 months and a cost increase of $45,000, but those estimates don’t fully reflect the effect of several oral drugs that were introduced after 2007 but did not come into widespread use during the entire study period, Dr. Howard and his associates noted (Health Aff. 2016 Sep 7;35[9]:1581-7).
Lung cancer patients experienced the smallest changes between the two time periods, with an increase in life expectancy of 3.9 months for those who received physician-administered anticancer drugs and a lifetime medical cost increase of $23,000. Patients with lung cancer who did not receive such drugs had increases of 0.7 months of life expectancy and $4,000 in lifetime medical costs.
The researchers used data from the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results–Medicare database, and all costs are adjusted to 2012 dollars. Data collection was supported by the California Department of Health and funding for the study was provided by Pfizer. Three of Dr. Howard’s five coinvestigators are Pfizer employees.