Click here to view more from Gastroenterology Data Trends 2024
AI and Machine Learning in IBD: Promising Applications and Remaining Challenges
Shirley Cohen-Mekelburg, MD, MS
Assistant Professor
Division of Gastroenterology
Michigan Medicine
Director of IBD
VA Ann Arbor Health Care System
Ann Arbor, Michigan
Dr. Cohen-Mekelburg has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.

Nearly 1 in 100 Americans have Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD), with up to 56,000 new cases being diagnosed each year.1 IBD is a complex disease with a myriad of presentations, possible treatment approaches, and patient outcomes. Artificial intelligence (AI)—a field of technology which began in the 1950s—refers to the ability of computers to learn and perform tasks that would have typically required human intelligence, while “machine learning” refers to the development of the algorithms that help AI learn patterns from data.2,3 The goal in many industries, including health care, is for AI to aid in and improve decision-making. Applications of AI including machine learning already greatly influence the oncology space, aiding in risk assessment, early diagnosis, prognosis, and treatment decision-making.4 Similar utilizations are being investigated to help improve the quality and efficiency of care for patients with IBD, but there is still much research to be done before we can fully leverage such tools in everyday practice.5
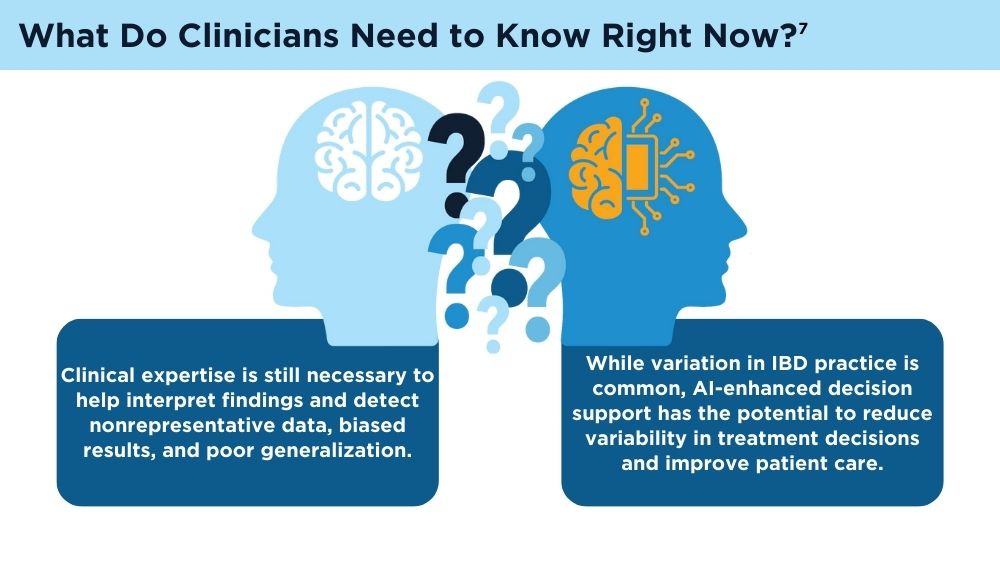
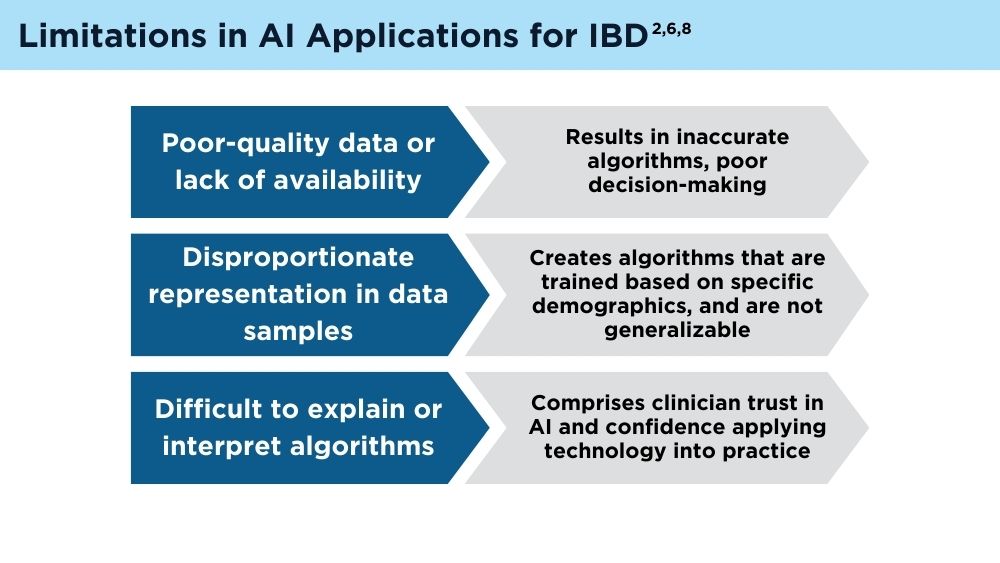
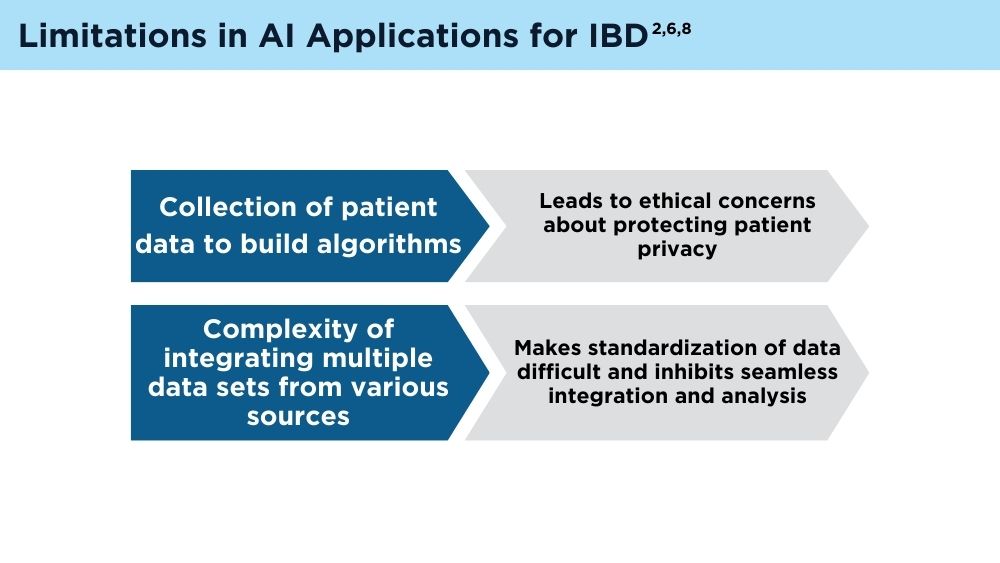
Although extensive progress in AI has been made since the turn of the century, several limitations remain. Poor-quality data sets may lead to inaccurate predictions, and it is difficult to generalize data sets to minority populations. In health care, clinicians must also understand and be able to interpret the algorithms in order to trust and apply them in practice. Lastly, and importantly, there are ethical concerns regarding patient privacy in data collection.6
1
Next Article:
More IBD & Intestinal Disorders News
- Does Bezlotoxumab Boost FMT Efficacy in IBD Patients With Recurrent CDI?
- Angiotensin Receptor Blockers May Lead to Worse Outcomes in Celiac Disease
- Common Crohn’s Immune Response to Gut Bacteria Suggests Therapeutic Target
- Guselkumab Efficacy in Crohn’s Disease Unaffected by Prior Biologic Use
- IBS: Understanding a Common Yet Misunderstood Condition
- Breath Gas Patterns Predict Response to Low FODMAP Diet
- Ultraprocessed Foods Associated With Relapse Risk in Crohn’s Disease
- Live Rotavirus Vaccine Safe for Newborns of Biologic-Treated Moms With IBD
Irritable Bowel Syndrome and Sleep