Caroline Ross, MD, and Alan Manivannan, MD; Senior Internal Medicine Residents, VABHS and BMC:
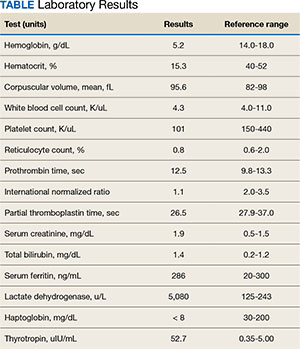
We noted several salient features in the history and physical examination. First, we sought to explain the bilateral lower extremity numbness and decreased vibratory sensation in the feet leading to falls. We also considered his anemia and thrombocytopenia with signs of hemolysis including elevated lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), low haptoglobin, and elevated total bilirubin; however, with normal coagulation parameters. These results initially raised our concern for a thrombotic microangiopathy (TMA) such as TTP. However, the peripheral smear lacked schistocytes, making this less likely. The combination of his neurologic symptoms and TMA-like laboratory findings but without schistocytes raised our concern for vitamin B12 deficiency. Vitamin B12 deficiency can cause a pseudo-TMA picture with laboratory finding similar to TTP; however, schistocytes are typically absent. We also considered the possibility of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) with bone marrow infiltration leading to anemia given the finding of a liver mass on his abdominal ultrasound and low reticulocyte index. However, this would not explain his hemolysis. We also considered chronic disseminated intravascular coagulation in the setting of a malignancy as a contributor, but again, the smear lacked schistocytes and his coagulation parameters were normal. Finally, we considered a primary bone marrow process such as myelodysplastic syndrome due to the bicytopenia with poor bone marrow response and smear with tear drop cells and elliptocytes. However, we felt this was less likely as this would not explain his hemolytic anemia.
Dr. Ulin:
To refine the differential diagnosis, we are joined by an expert clinician who was also not involved in the care of this patient to describe his approach to this case. Dr. Orlander, can you walk us through your clinical reasoning?
Jay Orlander, MD, MPH: Professor of Medicine, Section of General Internal Medicine, Boston University Chobanian & Avedisian School of Medicine, Associate Chief, Medical Service, VABHS:
I will first comment on the hepatic mass. The hypoechoic liver mass with peripheral vascularity suggests a growing tumor. The patient has a history of substance use disorder with alcohol and treated HCV. He remains at increased risk for HCC even after prior successful HCV treatment and has 2 of 4 known risk factors for developing HCC— diabetes mellitus and alcohol use—the other 2 being underlying metabolic dysfunctionassociated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) and the presence of hepatic fibrosis, which we have not yet assessed. Worsening liver function can lead to cognitive issues and alcohol to peripheral neuropathy, but his story is not consistent with this. For his liver mass, I recommend a nonurgent magnetic resonance image for further evaluation.
Next, let’s consider his markedly elevated thyrotropin (TSH). Cognitive impairment along with lethargy, fatigue, and decreased exercise tolerance can be prominent features in severe hypothyroidism, but this diagnosis would not explain his hematologic findings. 1
I view the principal finding of his laboratory testing as being that his bone marrow is failing to maintain adequate blood elements. He has a markedly low hematocrit along with low platelets and low-normal white blood cell counts. There is an absence of schistocytes on the blood smear, and after correcting his reticulocyte count for his degree of anemia (observed reticulocyte percentage [0.8%] x observed hematocrit [15.3%] / expected hematocrit [40%]), results in a reticulocyte index of 0.12, which is low. This suggests his bone marrow is failing to manufacture red blood cells at an appropriate rate. His haptoglobin is unmeasurable, so there is some free heme circulating. Hence, I infer that hemolysis and ineffective erythropoiesis are both occurring within the bone marrow, which also explains the slight elevation in bilirubin.