Results
We reviewed 8779 patient records. A random sample of 10% of the records of each diagnosis code was taken and 876 charts were reviewed. Of the charts reviewed, 351 patients met the inclusion criteria and were included in the analysis. A goal of 90% was established as the target for prescriber adherence for the study based on author consensus for a reasonable goal. Of the 351 evaluated charts, 62 (16.1%) were pediatric patients (aged < 19 years) and 289 (83.9%) were adults (aged ≥ 19 years). Fifty-two (84%) of the pediatric charts and 249 (86%) of the adult charts demonstrated prescribers had appropriately followed guidelines for a combined total of 301 of the 351 charts and an overall adherence rate of 86%. This was 4 points below the established goal of 90%, warranting further investigation. An analysis of prescribers and locations revealed no trends or patterns of nonadherence. A prescriber survey and educational intervention were designed and disseminated to all prescribers at the facility with the approval and assistance of the chief of medicine.
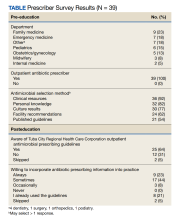
Thirty-nine prescribers responded to the survey. In the pre-educational survey, clinical resources were the most common source of guidance with 36 prescribers (92%) indicating they used them to make an appropriate selection of an antimicrobial; 32 (82%) used personal knowledge, 30 (77%) used culture results, and 24 (62%) used facility guidelines. This was consistent with the posteducational questions: 12 (31%) indicated they were not aware of the facility guidelines before the educational intervention.
After the informational section of the survey, 9 prescribers (23%) indicated they would always use the guidelines, 17 (44%) sometimes, 3 (8%) occasionally, 8 (21%) indicated that they already used the guidelines, and 2 (5%) did not provide an answer (Table).Discussion
This study’s objective was to evaluate prescriber adherence to the facility outpatient prescribing guidelines after they were implemented in 2019 and to plan for interventions if necessary. Overall prescriber adherence was high with 86% of the sampled charts adherent. This was below the goal of 90%, so evaluation of the nonadherent charts was warranted for the determination of any patterns to guide the planned interventions with the facility prescribers. However, no trends were identified, so the intervention was designed as a general survey and educational session for all prescribers. Overall prescriber response was positive, with a total of 34 responding prescribers (87%) indicating a willingness to use the guidelines.
Limitations
This is a retrospective observational study performed through chart review that allowed for frequency analysis but did not allow for statistical analysis, so the significance of results cannot be obtained. Additionally, this study was not able to compare rates of adherence before and after the educational intervention, so the effectiveness of the intervention cannot be assessed.
Conclusions
This retrospective observational study’s data demonstrate that prescribers are adhering at a high rate to recommended empiric antimicrobials for outpatient treatment with an 86% adherence rate. Response to educational intervention indicated a larger proportion of prescribers than previously will use the guidelines. However, the impact this will have on appropriate prescribing rates in the future could not be assessed during this study.