Evaluation of oral antineoplastic agent (OAN) adherence patterns have identified correlations between nonadherence or over-adherence and poorer disease-related outcomes. Multiple studies have focused on imatinib use in chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) due to its continuous, long-term use. A study by Ganesan and colleagues found that nonadherence to imatinib showed a significant decrease in 5-year event-free survival between 76.7% of adherent participants compared with 59.8% of nonadherent participants.1 This study found that 44% of patients who were adherent to imatinib achieved complete cytogenetic response vs only 26% of patients who were nonadherent. In another study of imatinib for CML, major molecular response (MMR) was strongly correlated with adherence and no patients with adherence < 80% were able to achieve MMR.2 Similarly, in studies of tamoxifen for breast cancer, < 80% adherence resulted in a 10% decrease in survival when compared to those who were more adherent.3,4
In addition to the clinical implications of nonadherence, there can be a significant cost associated with suboptimal use of these medications. The price of a single dose of OAN medication may cost as much as $440.5
The benefits of multidisciplinary care teams have been identified in many studies.6,7 While studies are limited in oncology, pharmacists provide vital contributions to the oncology multidisciplinary team when managing OANs as these health care professionals have expert knowledge of the medications, potential adverse events (AEs), and necessary monitoring parameters.8 In one study, patients seen by the pharmacist-led oral chemotherapy management program experienced improved clinical outcomes and response to therapy when compared with preintervention patients (early molecular response, 88.9% vs 54.8%, P = .01; major molecular response, 83.3% vs 57.6%, P = .06).9 During the study, 318 AEs were reported, leading to 235 pharmacist interventions to ameliorate AEs and improve adherence.
The primary objective of this study was to measure the impact of a pharmacist-driven OAN renewal clinic on medication adherence. The secondary objective was to estimate cost-savings of this new service.
Methods
Prior to July 2014, several limitations were identified related to OAN prescribing and monitoring at the Richard L. Roudebush Veterans Affairs Medical Center in Indianapolis, Indiana (RLRVAMC). The prescription ordering process relied primarily on the patient to initiate refills, rather than the prescriber OAN prescriptions also lacked consistency for number of refills or quantities dispensed. Furthermore, ordering of antineoplastic products was not limited to hematology/oncology providers. Patients were identified with significant supply on hand at the time of medication discontinuation, creating concerns for medication waste, tolerability, and nonadherence.
As a result, opportunities were identified to improve the prescribing process, recommended monitoring, toxicity and tolerability evaluation, medication reconciliation, and medication adherence. In July of 2014, the RLRVAMC adopted a new chemotherapy order entry system capable of restricting prescriptions to hematology/oncology providers and limiting dispensed quantities and refill amounts. A comprehensive pharmacist driven OAN renewal clinic was implemented on September 1, 2014 with the goal of improving long-term adherence and tolerability, in addition to minimizing medication waste.
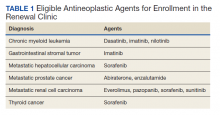
Patients were eligible for enrollment in the clinic if they had a cancer diagnosis and were concomitantly prescribed an OAN outlined in Table 1. All eligible patients were automatically enrolled in the clinic when they were deemed stable on their OAN by a hematology/oncology pharmacy specialist. Stability was defined as ≤ Grade 1 symptoms associated with the toxicities of OAN therapy managed with or without intervention as defined by the Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE) version 4.03. Once enrolled in the renewal clinic, patients were called by an oncology pharmacy resident (PGY2) 1 week prior to any OAN refill due date. Patients were asked a series of 5 adherence and tolerability questions (Table 2) to evaluate renewal criteria for approval or need for further evaluation. These questions were developed based on targeted information and published reports on monitoring adherence.10,11 Criteria for renewal included: < 10% self-reported missed doses of the OAN during the previous dispensing period, no hospitalizations or emergency department visits since most recent hematology/oncology provider appointment, no changes to concomitant medication therapies, and no new or worsening medication-related AEs. Patients meeting all criteria were given a 30-day supply of OAN. Prescribing, dispensing, and delivery of OAN were facilitated by the pharmacist. Patient cases that did not meet criteria for renewal were escalated to the hematology/oncology provider or oncology clinical pharmacy specialist for further evaluation.