Data Collection
On procedure day, all participants completed the anxiety scale as well as a VAS pain scale (which is the MRVAMC standard of care), preoperatively and postprocedure. Envelopes were opened prior to going into the procedure room to prevent prior knowledge of who was assigned to the music group. Participants in the music intervention group listened to their preselected music on a portable CD player in the procedure room. The music was played softly so the patient could still hear and respond to the physicians instructions during the procedure. The no-music group received everything that the music intervention group received except for music (standard care throughout procedure, which consisted of nurse monitoring, measures to reduce fear and anxiety, and comfort measures). Procedures were performed with local anesthesia; neither group received moderate sedation.
Gender, age, and self-reported pain scores (before and after the lumber RFL procedure) were recorded in the patient’s chart and entered into the study database. Patients in both groups were queried before and after the procedure using the VAS to measure their pain and anxiety levels. Participants in the music intervention group were asked whether they felt that the music helped. They also were asked to provide feedback about their experience. Data were stored in locked filing cabinets, and all forms were de-identified.
Statistical Analysis
SAS version 9.2 (Cary, NC) was used for all analyses. Data were inspected for out-of-range values. The Fisher exact test was used to compare groups on categorical measures. An independent sample t test was used to compare groups on the age variable. Difference scores (formed by subtracting the after score from the before score) were analyzed using paired t tests. Analysis of covariance was used to test for significant group differences on the outcome variables of pain and anxiety with group as the independent variable and the preprocedure measure as the covariate. The level of significance was set at .05, and all testing was 2 sided.
Results
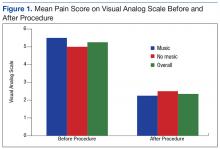
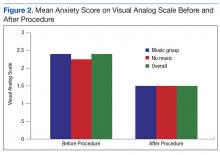
Of the 60 consenting patients, 44 participated in the study.Twenty-three were randomized to the music intervention and 21 to the no-music control group. Both pain and anxiety were significantly reduced (P < .0001) in the total sample (n = 44). The mean (SD) decrease in pain for all participants was 2.80 points (2.31) on a VAS of 0 to 10 and 0.86 points (0.93) decrease in anxiety. In the music intervention group, the mean decrease in pain and anxiety was 3.22 (2.66) and 1.00 (0.85), respectively. In the no-music group, the mean decrease in pain and anxiety was 2.33 (1.80) and 0.69 (1.00), respectively. The magnitude of pain decrease was larger in the music intervention group; however, the difference did not reach statistical significance.
Discussion
Although there was not a statistically significant difference in pain or anxiety reduction due to group assignment, a 2-point reduction in self-reported pain or anxiety may be considered clinically important and has been supported in older studies.6 Importantly, 87% of participants in the music intervention group reported that listening to music was helpful during the procedure (Figure 1).
Anxiety levels were not as high as expected when measured before and after the procedure, perhaps due to improvements in patient education and continuity of care (Figure 2). Since all participants were returning patients, they already were familiar with the procedure and the staff. Staff turnover rate is very low at this clinic, which may have contributed to the low anxiety rates among participants at baseline. Other contributing factors included good communication, expert technique, and teamwork.
During the study, few negative comments were noted. One participant did not hear the music due to faulty equipment setup. Another participant commented that the physician doing the procedure made negative remarks about the music the patient selected. A third participant commented that the music was too loud, and he was unable to hear the doctor’s instructions, indicating a need for guidelines.
There were many positive comments by participants in the music intervention group. Nurses reported comments such as “The music really helps”; “The music was great, but rock ‘n’ roll would be better”; and “Can I bring my own [music] next time?” Many patients returning for procedures frequently asked, “Where is the music?”
Limitations
Of the 60 consenting patients, only 44 participated, possibly lowering the power of the study to detect significant findings. During the study, the physician staff was reduced, resulting in fewer RFLs performed and causing the study to take longer to conduct and with fewer opportunities to recruit participants.
The CD players used for the study were old, and because earbuds could not be used, volume was difficult to modulate consistently. Earbuds were not used because patient participation was required during the procedure. Also, having only 3 music genres to choose from limited the participant’s choice.