Patient-applied treatments
- Podofilox 0.5% solution or gel. Patients should apply podofilox solution with a cotton swab, or podofilox gel with a finger, to visible genital warts twice a day for 3 days, followed by 4 days of no therapy. This cycle may be repeated, as necessary, for up to 4 cycles. The health care provider may apply the initial treatment to demonstrate the proper application technique and identify which warts should be treated.
- Imiquimod 5% cream. Patients should apply imiquimod cream once daily at bedtime, 3 times a week for up to 16 weeks. The treatment area should be washed with soap and water 6 to 10 hours after the application.
Provider-administered treatments
- Cryotherapy with liquid nitrogen or cryoprobe. Repeat applications every 1 to 2 weeks.
- Podophyllin resin 10% to 25% in a compound tincture of benzoin. A small amount should be applied to each wart and allowed to air-dry. The treatment can be repeated weekly, if necessary. To avoid the possibility of complications associated with systemic absorption and toxicity, some specialists recommend that application be limited to ≤0.5 mL of podophyllin or an area of <10 cm2 of warts per session. Some specialists suggest the preparation should be thoroughly washed off 1 to 4 hours after application to reduce local irritation. The safety of podophyllin during pregnancy has not been established.
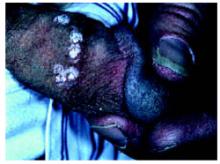
- Trichloroacetic acid (TCA): a small amount should be applied only to warts and allowed to dry, at which time a white “frosting” develops (Figure 3). This treatment can be repeated weekly, if necessary.
- Surgical removal either by tangential scissor excision, tangential shave excision, curettage, or electrosurgery.
FIGURE 3
Treatment of genital warts