Indolent systemic mastocytosis (ISM) can cause potentially debilitating symptoms due to uncontrolled proliferation and activation of abnormal mast cells, which can accumulate in the skin, digestive tract, bone marrow and other organs.1 Patients can experience a diverse range of mast cell mediator-related symptoms, including skin spots, itching, diarrhea, fatigue, brain fog and bone pain.1,2 In about 95% of cases, the underlying driver of disease is the KIT D816V mutation. 1,3,4,5
Until recently, there were no approved therapies for ISM. The condition has been primarily managed with symptom-directed treatments such as antihistamines and cromolyn sodium, as well as the avoidance of known triggers.1
“Patients with ISM may take multiple symptom-directed therapies and visit healthcare providers frequently due to their disease,” said Anne Maitland, MD, PhD, allergist/immunologist at Comprehensive Allergy & Asthma Care. “A therapy that targets KIT D816V has been considered a medical need for patients with ISM.”

First and Only FDA-Approved Therapy for ISM
In May 2023, AYVAKIT® (avapritinib) became the first FDA-approved therapy for adults with ISM that targets KIT D816V, a primary driver of disease in about 95% of cases.3,4,5,7 AYVAKIT is not recommended for patients with ISM with platelet counts <50 × 109/L.7 The recommended dose for patients with ISM is 25 mg, taken orally once daily. KIT D816V testing is not required for AYVAKIT treatment.
Please see Important Safety Information below and click here for full Prescribing Information.
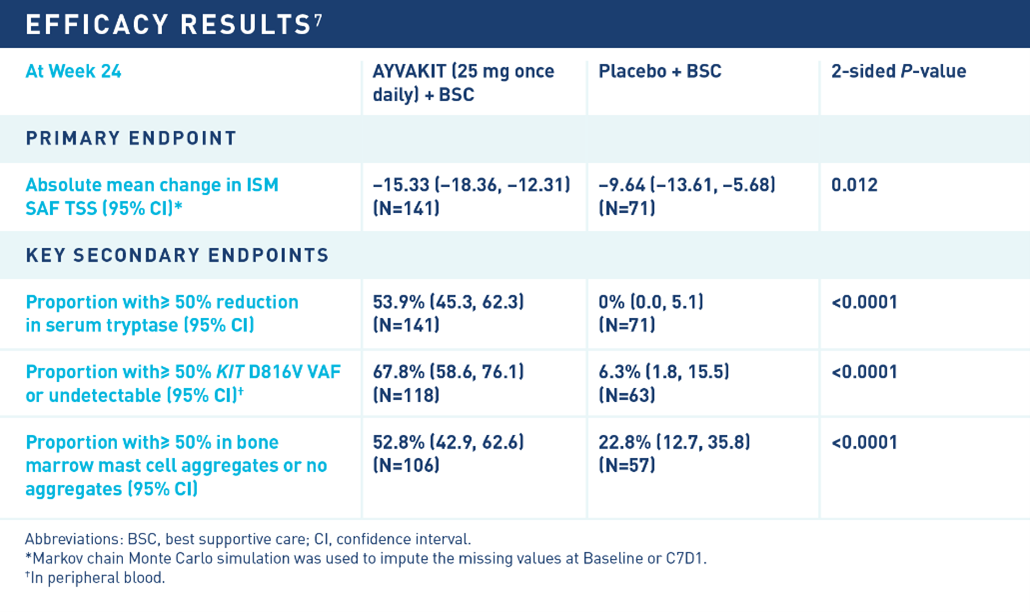
The approval of AYVAKIT in ISM was based on data from PIONEER, a randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind phase 2 trial7 and the largest study conducted in ISM to date. Results were published in the May 23, 2023 issue of NEJM Evidence.8
The PIONEER trial enrolled adults with moderate to severe ISM symptoms not adequately controlled on best supportive care (BSC) alone, and the study evaluated the safety and efficacy of AYVAKIT 25 mg once daily plus BSC (AYVAKIT arm; n=141) versus placebo plus BSC (placebo arm; n=71) over 24 weeks.7,8 Patient characteristics were similar between both treatment arms, and 93% of patients who received AYVAKIT had the KIT D816V mutation. BSC medicines allowed in the trial included anti-immunoglobulin E antibody (omalizumab), glucocorticoids, cromolyn sodium, H1 antihistamines, H2 antihistamines, leukotriene inhibitors and proton pump inhibitors, which were optimized prior to patients starting the study.8
The Indolent Systemic Mastocytosis Symptom Assessment Form (ISM-SAF), a validated symptom assessment tool, was used to evaluate ISM signs and symptoms reported by patients in the trial.7 Individual symptom severity scores were combined to calculate the total symptom score (TSS). The ISM-SAF assessed skin (spots, itching, flushing), neurocognitive (brain fog, headache, dizziness), gastrointestinal (abdominal pain, diarrhea, nausea) and other (bone pain, fatigue) symptoms.
AYVAKIT demonstrated significant improvements versus placebo in the primary and all key secondary endpoints of the PIONEER trial. At 24 weeks, AYVAKIT achieved a significant reduction in the ISM-SAF TSS compared to placebo, and more than half of evaluated patients treated with AYVAKIT experienced ≥50% reduction in serum tryptase, KIT D816V variant allele fraction and bone marrow mast cell aggregates.
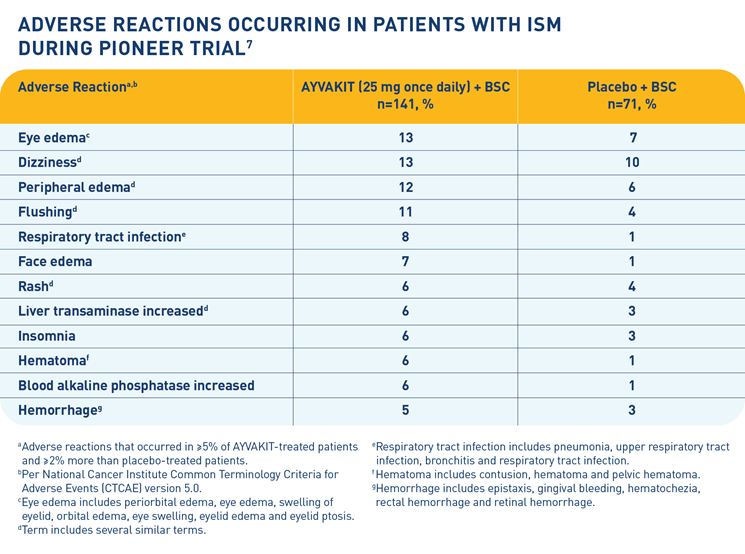
The most common adverse reactions (≥10%) for AYVAKIT were eye edema, dizziness, peripheral edema and flushing. Of all adverse reactions, 55% were Grade 1, 38% were Grade 2, and 7% were Grade 3. Among patients with edema adverse reactions, 95% were Grade 1 and 5% were Grade 2, and among patients with hemorrhage adverse reactions, 86% were Grade 1 and 14% were Grade 2. Serious adverse reactions for AYVAKIT occurred in 1 patient (0.7%) due to pelvic hematoma, and permanent discontinuation of AYVAKIT due to adverse reactions occurred in 1 patient (0.7%) due to dyspnea and dizziness. Dose interruptions of AYVAKIT due to an adverse reaction occurred in 5% of patients.
Helping Address the Medical Needs of Patients with ISM
ISM can lead to persistent and potentially debilitating symptoms, as well as frequent visits to healthcare providers and the use of multiple symptom-directed treatments. Historically, there were no approved therapies for ISM.
“The FDA approval of AYVAKIT expands treatment options for adults with ISM,” said Dr Maitland. “This regulatory milestone was based on the clinical efficacy of AYVAKIT across multiple measures of disease symptoms and mast cell burden, and the therapy’s tolerability profile relative to the placebo arm. PIONEER data support adding AYVAKIT to symptom-directed treatment in patients who continue to experience ISM symptoms.”
To learn more, visit https://www.ayvakithcp.com/ism/.
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION AND INDICATION
Intracranial Hemorrhage—Serious intracranial hemorrhage (ICH) may occur with AYVAKIT treatment; fatal events occurred in <1% of patients. No events of ICH occurred in the 246 patients with ISM who received any dose of AYVAKIT in the PIONEER study.
Monitor patients closely for risk factors of ICH which may include history of vascular aneurysm, ICH or cerebrovascular accident within the prior year, concomitant use of anticoagulant drugs, or thrombocytopenia.
Symptoms of ICH may include headache, nausea, vomiting, vision changes, or altered mental status. Advise patients to seek immediate medical attention for signs or symptoms of ICH.
Permanently discontinue AYVAKIT if ICH of any grade occurs.
Cognitive Effects—Cognitive adverse reactions can occur in patients receiving AYVAKIT and occurred in 7.8% of patients with ISM who received AYVAKIT + best supportive care (BSC) versus 7.0% of patients who received placebo + BSC; <1% were Grade 3. Depending on the severity, withhold AYVAKIT and then resume at the same dose, or permanently discontinue AYVAKIT.
Photosensitivity—AYVAKIT may cause photosensitivity reactions. In all patients treated with AYVAKIT in clinical trials (n=1049), photosensitivity reactions occurred in 2.5% of patients. Advise patients to limit direct ultraviolet exposure during treatment with AYVAKIT and for one week after discontinuation of treatment.
Embryo-Fetal Toxicity—AYVAKIT can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. Advise pregnant women of the potential risk to a fetus. Advise females and males of reproductive potential to use an effective method of contraception during treatment with AYVAKIT and for 6 weeks after the final dose. Advise women not to breastfeed during treatment with AYVAKIT and for 2 weeks following the final dose.
Adverse Reactions—The most common adverse reactions (≥10%) in patients with ISM were eye edema, dizziness, peripheral edema, and flushing.
Drug Interactions—Avoid coadministration of AYVAKIT with strong or moderate CYP3A inhibitors or inducers.
To report suspected adverse reactions, contact Blueprint Medicines Corporation at 1-888-258-7768 or the FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or http://www.fda.gov/medwatch.
AYVAKIT is available in a 25 mg tablet.
Please click here to see the full Prescribing Information for AYVAKIT.
AYVAKIT (avapritinib) is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with indolent systemic mastocytosis (ISM).
Limitations of Use: AYVAKIT is not recommended for the treatment of patients with ISM with platelet counts of <50 × 109/L.
This promotional content was developed by Blueprint Medicines Corporation, the manufacturer of AYVAKIT.
Blueprint Medicines and associated logos are trademarks of Blueprint Medicines Corporation.
© 2024 Blueprint Medicines Corporation.
References
1. Pardanani A. Am J Hematol. 2023;98(7):1097-1116.
2. Gulen T. J Int Med. 2016;279(3):211-228.
3. Garcia-Montero AC et al. Blood. 2006;108(7):2366-2372.
4. Ungerstedt J et al. Cancers. 2022;14(16):3942.
5. Kristensen T et al. Am J Hematol. 2014;89(5):493-498.
6. Data on file. Blueprint Medicines Corporation, Cambridge, MA. 2024.
7. AYVAKIT (avapritinib). Prescribing information. Blueprint Medicines; 2023. Accessed April 8, 2024. https://www.blueprintmedicines.com/wp-content/uploads/uspi/AYVAKIT.pdf
8. Gotlib J et al. NEJM Evid. 2023;2(6). Published online May 23, 2023. doi:10.1056/EVIDoa2200339
04/2024 USBPM23.0002.2
