How to integrate STI preventioninto the primary care encounter
A key resource for learning to recognize the signs and symptoms of STIs, to correctly diagnose them, and to treat them according to CDC guidelines can be found at www.cdc.gov/std/tg2015/default.htm.5 Equally important is to integrate the prevention of STIs into the clinical routine by using a 4-step approach: risk assessment, risk reduction (counseling and chemoprevention), screening, and vaccination.
Risk assessment. The first step in prevention is taking a sexual history to accurately assess a patient’s risk for STIs. The CDC provides a tool (www.cdc.gov/std/products/provider-pocket-guides.htm) that can assist in gathering information in a nonjudgmental fashion about 5 Ps: partners, practices, protection from STIs, past history of STIs, and prevention of pregnancy.
Risk reduction. Following STI risk assessment, recommend risk-reduction interventions, as appropriate. Notable in the new Task Force recommendation are behavioral counseling methods that work. Additionally, when needed, pre-exposure prophylaxis with effective antiretroviral agents can be offered to those at high risk of HIV.6
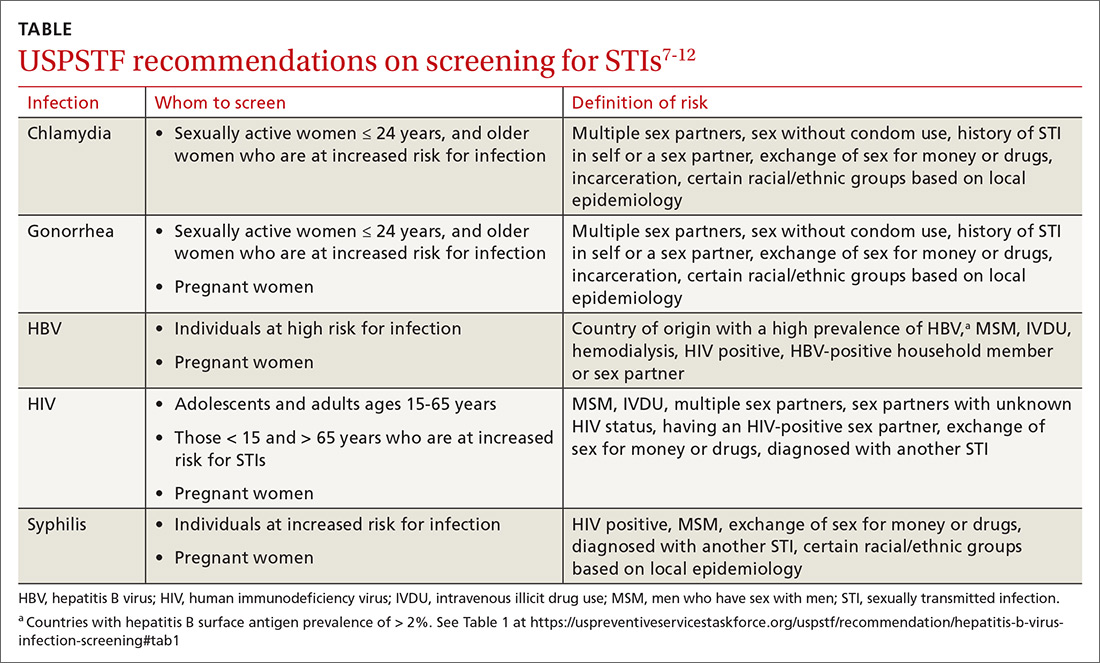
Screening. Task Force recommendations for STI screening are described in the TABLE.7-12 Screening for HIV, chlamydia, gonorrhea, syphilis, and HBV are also recommended for pregnant women. And, although pregnant women are not specifically mentioned in the recommendation on chlamydia screening, it is reasonable to include it in prenatal care testing for STIs.
The Task Force has made an “I” statement regarding screening for gonorrhea and chlamydia in males. This does not mean that screening should be avoided, but only that there is insufficient evidence to support a firm statement regarding the harms and benefits in males. Keep in mind that this applies to asymptomatic males, and that testing and preventive treatment are warranted after documented exposure to either infection.
The Task Force recommends against screening for genital herpes, including in pregnant women, because of a lack of evidence of benefit from such screening, the high rate of false-positive tests, and the potential to cause anxiety and harm to personal relationships.
Continue to: Although hepatitis C virus...