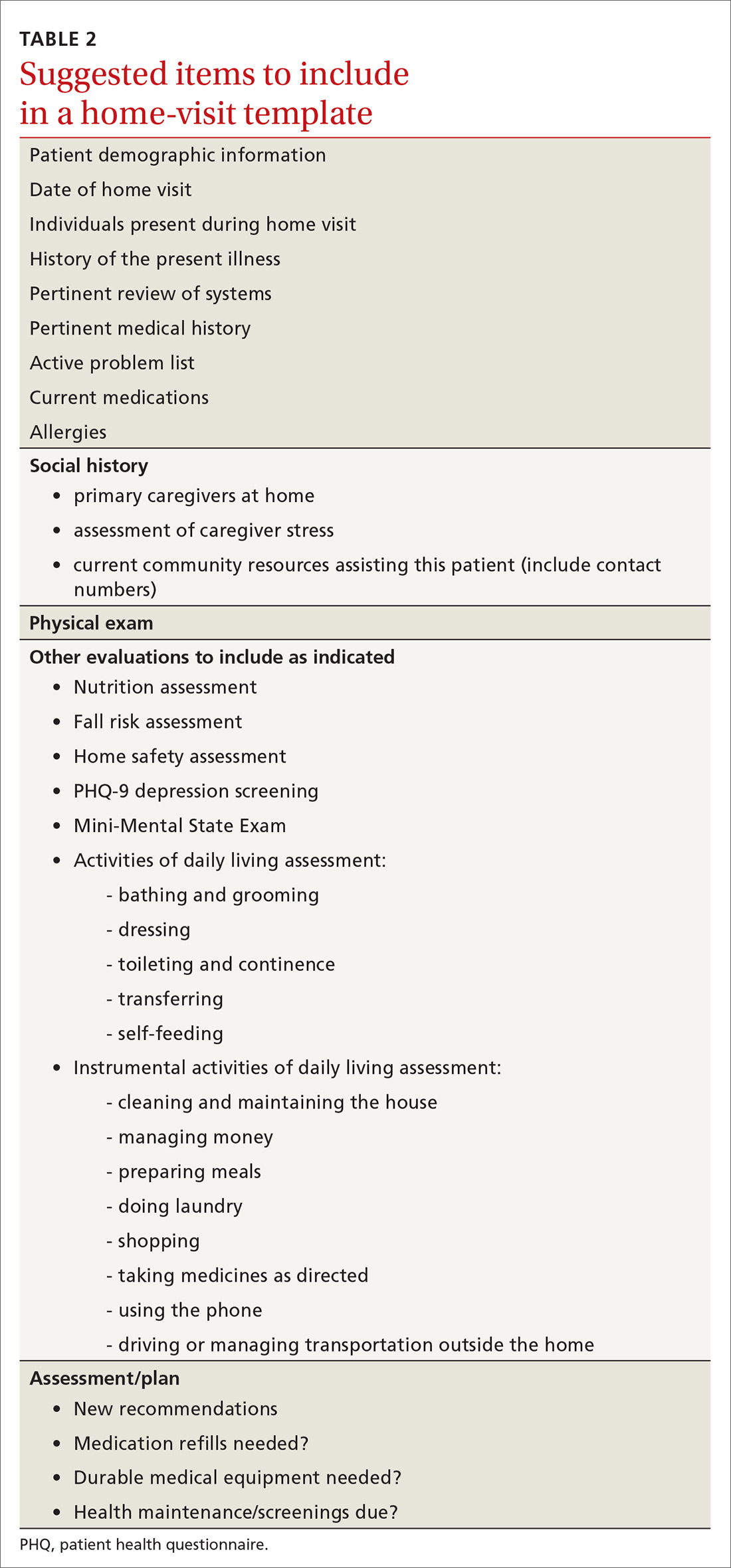
Documentation and reimbursement. While individual electronic medical records may require use of particular forms of documentation, using a home visit template when possible can be extremely helpful (TABLE 2). A template not only assures thoroughness and consistency (pharmacy, home health contacts, billing information) but also serves as a prompt to survey the patient and the caregivers about nonmedical, but essential, social and well-being services. The document should be as simple and user-friendly as possible.
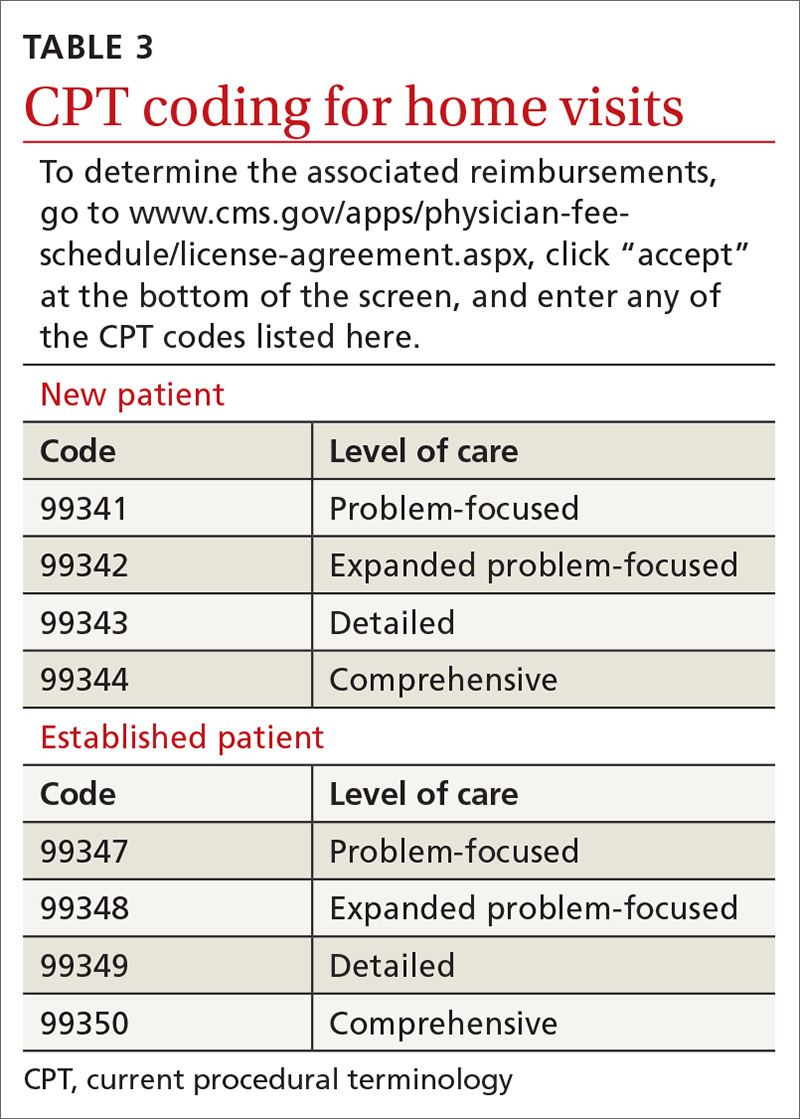
Not all assessments will be able to be done at each visit but seeing them listed in the template can be helpful. Billing follows the same principles as for office visits and has similar requirements for documentation. Codes for the most common types of home visits are listed in TABLE 3.
Where can I get help?
Graduates of family medicine residency programs are required to receive training in home visits by the Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education (ACGME). Current ACGME program requirements stipulate that “residents must demonstrate competence to independently diagnose, manage, and integrate the care of patients of all ages in various outpatient settings, including the FMP [family medicine practice] site and home environment,” and “residents must be primarily responsible for a panel of continuity patients, integrating each patient’s care across all settings, including the home ...” [emphasis added].34
For those already in practice, one of the hardest parts of doing home visits is feeling alone, especially if few other providers in your community engage in home care. As you run into questions and challenges with incorporating home care of patients into your practice, one excellent resource is the American Academy of Home Care Medicine (www.aahcm.org/). Founded in 1988 and headquartered in Chicago, it not only provides numerous helpful resources, but serves as a networking tool for physicians involved in home care.
This unprecedented pandemichas allowed home visits to shine
As depicted in our opening patient case, patients who have high-risk conditions and those who are older than 65 years of age may be cared for more appropriately in a home visit rather than having them come to the office. Home visits may also be a way for providers to “lay eyes” on patients who do not have technology available to participate in virtual visits.
Before performing a home visit, inquire as to whether the patient has symptoms of COVID-19. Adequate PPE should be donned at all times and social distancing should be practiced when appropriate. With adequate PPE, home visits may also allow providers to care for low-risk patients known to have COVID-19 and thereby minimize risks to staff and other patients in the office. JFP
CORRESPONDENCE
Curt Elliott, MD, Prisma Health USC Family Medicine Center, 3209 Colonial Drive, Columbia, SC 29203; curtis.elliott@uscmed.sc.edu.