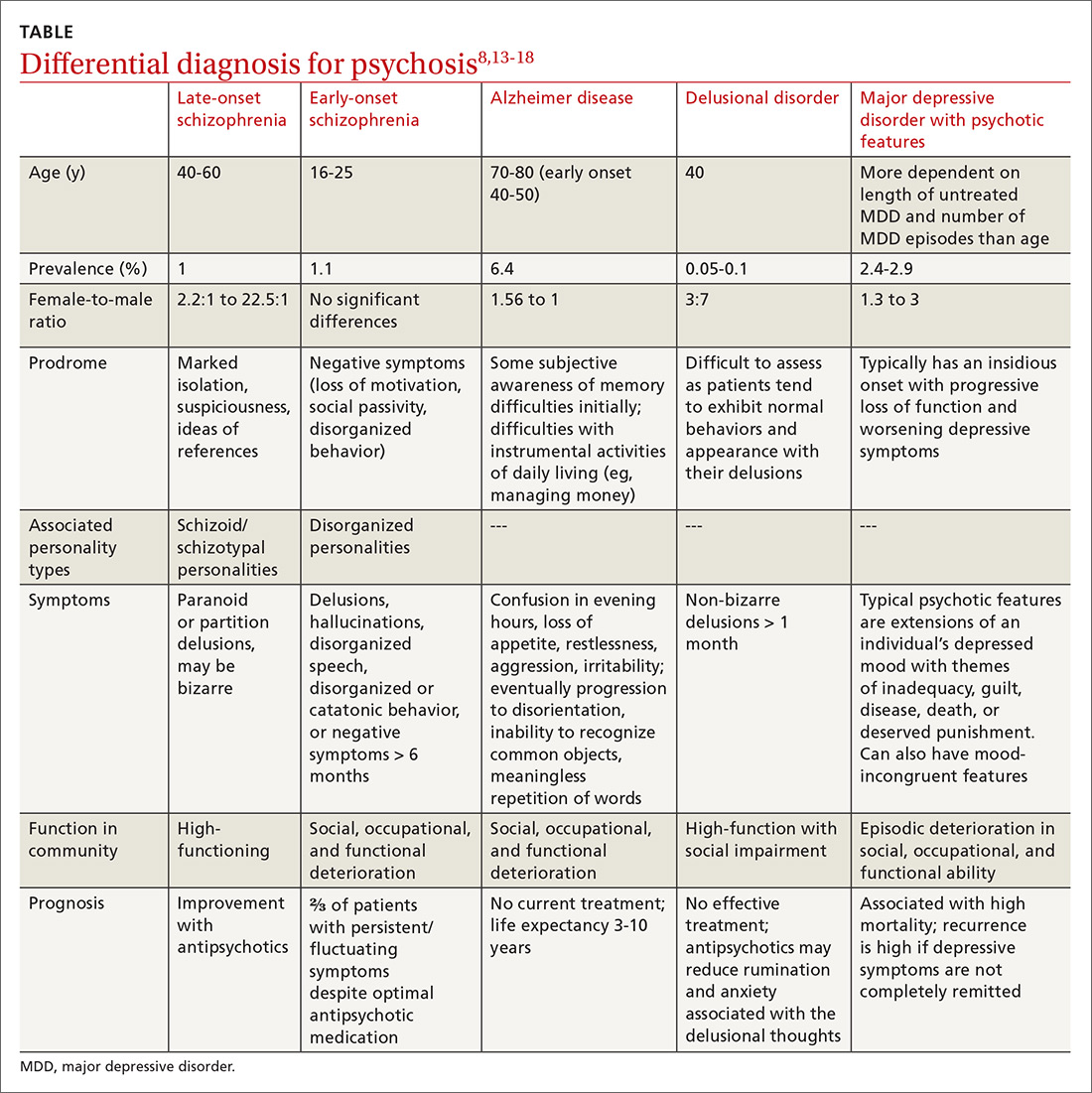
Differential diagnosis. When psychosis appears later in life, it is important to consider a broad differential (TABLE13-18), which includes the following:
Alzheimer disease. LOS can be easily differentiated from psychosis associated with Alzheimer disease or dementia through findings from neuropsychologic assessments and brain imaging. The initial first-line assessment for Alzheimer disease includes determining time course of daily living impairment and memory with follow-up brain imaging. Magnetic resonance imaging of patients with Alzheimer disease shows clear atrophy of the medial temporal lobes and general brain atrophy.19 Other than hypoperfusion in the frontal and temporal area, brain imaging of patients with LOS will not reveal any pathology.1
Delusional disorder and LOS are often more challenging to differentiate because symptoms can overlap, and many of the negative symptoms that would otherwise help clinicians diagnose schizophrenia in a younger population are absent in LOS. The milder symptoms of LOS may also lead clinicians to favor a diagnosis of delusional disorder. However, the following differences can help physicians differentiate between LOS and delusional disorder. Delusional disorder20-22:
- often will include paranoid beliefs, but these beliefs will not be bizarre, and the patient’s daily functioning will not be impaired, whereas patients with schizophrenia would have an increase in isolation and impairment in functioning that tends to be distinct from baseline.
- is more rare than schizophrenia. Delusional disorder has a prevalence of 0.05% to 0.1% compared to 1% for schizophrenia.
Major depressive disorder (MDD) with psychotic features. Major depressive disorder with psychotic features is an important differential to consider in this setting because the treatment intervention can be considerably different. Among patients who have MDD with psychotic features, a significant mood component is present, and treatment typically focuses on optimizing a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI); depending on severity, electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) also may be warranted.19
Continue to: For patients with LOS...