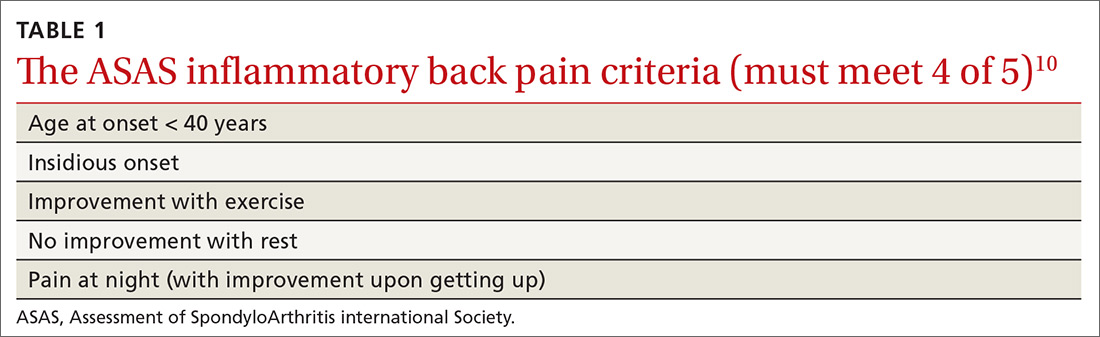
In addition, AS predominantly affects people in the third and fourth decades of life, but as many as 5% of patients of all ages with chronic back pain (> 3 months) can be classified as having AS.8 In patients who have IBP features, 14% can be classified as having axSpA.9 Therefore, it is important to recognize the features of IBP (TABLE 110). The presence of 4 of the 5 of IBP features has a sensitivity of 77% and a specificity of 91.7% for IBP.10
A different kind of back pain. The vast majority of patients presenting with low back pain will have features of mechanical back pain, which include improvement with rest, mild and short-lived morning stiffness and/or pain upon waking, and the absence of inflammatory markers. Those with axSpA, on the other hand, are more likely to report improvement of pain with exercise, no improvement with rest, and pain at night with improvement upon rising. While the presence of IBP features alone isn’t diagnostic for nr-axSpA or AS, such features should increase your suspicion, especially when such features are present in younger patients.
Physical exam findings
Physical exam findings are neither sensitive nor specific for the diagnosis of an axSpA disorder, but can help build a case for one. The physical exam can also assist in identifying comorbid conditions including uveitis, psoriasis, dactylitis, and enthesitis. Experts do not recommend using serial measurements of axial range of motion because they are time-consuming, and normative values are highly variable.
On examination of the peripheral joints and feet, note any swollen, tender, or deformed joints, as well as any dactylitis. Although any enthesis can be affected in axSpA, the insertional points of the Achilles and the plantar fascia are the most typical,1 so pay particular attention to these areas. On skin exam, note any evidence of psoriatic manifestations. Refer all patients with suspected uveitis to an ophthalmologist for confirmation of the diagnosis.
Lab studies: Not definitive, but helpful
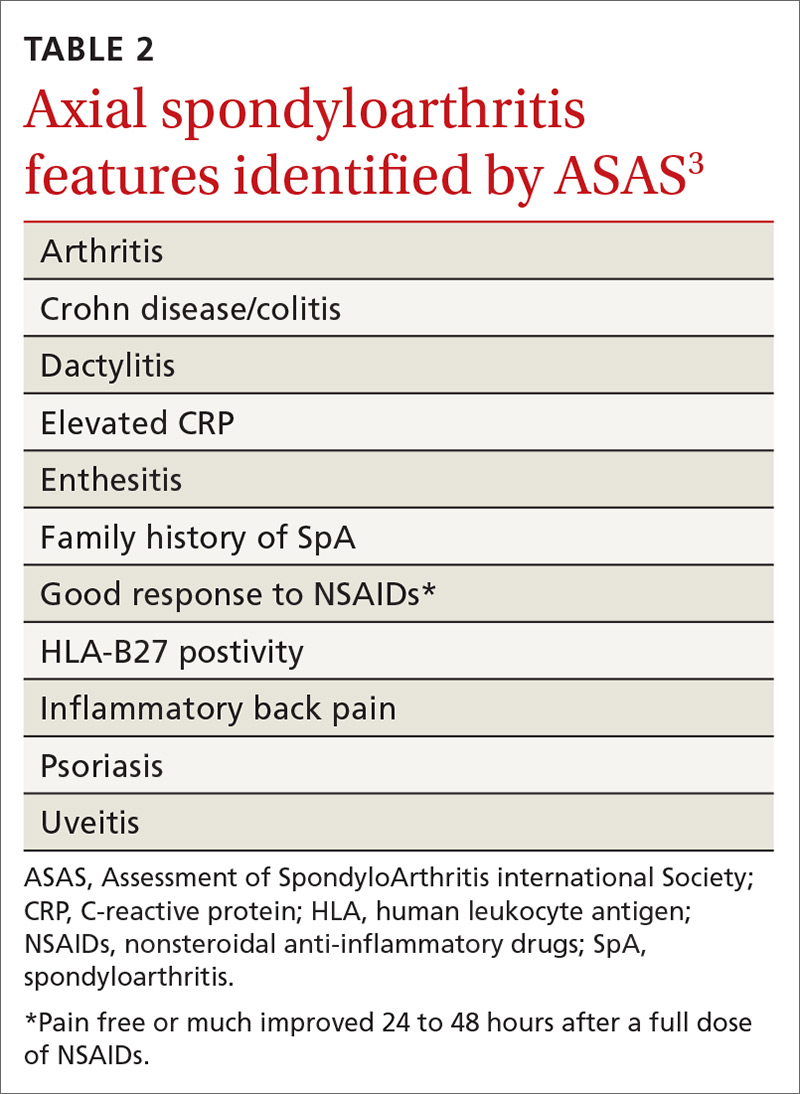
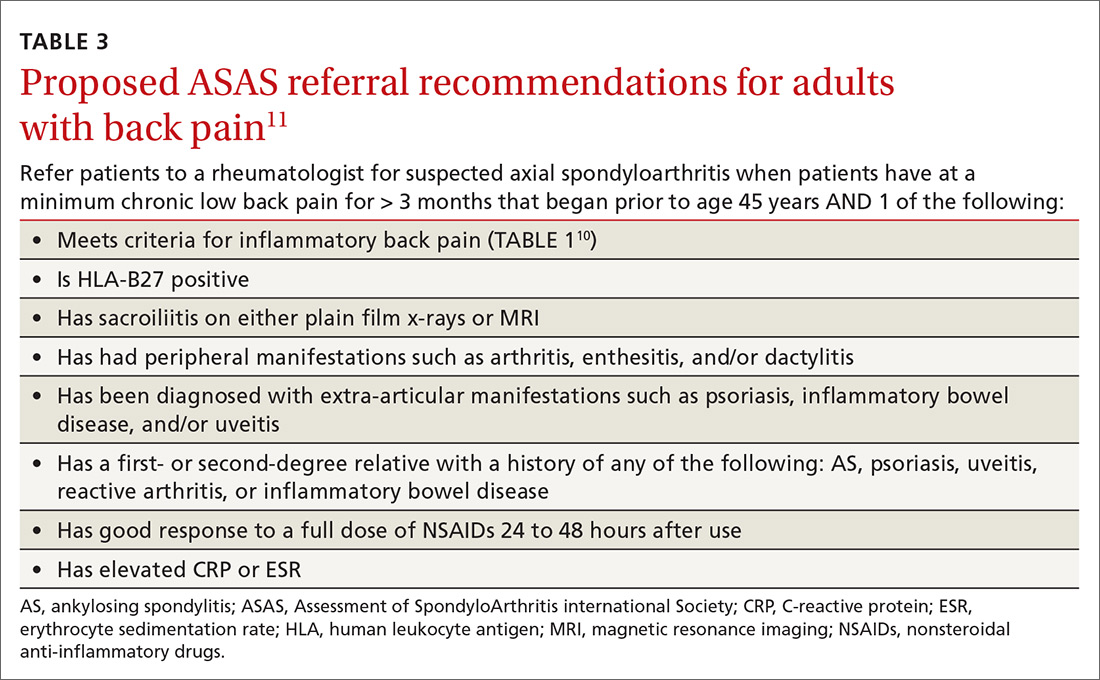
No laboratory studies confirm a diagnosis of nr-axSpA or AS; however, 2 studies—C-reactive protein (CRP) and HLA-B27—are important, as levels are listed as part of ASAS’s axSpA features (TABLE 23) and are factors that should be considered when deciding whether a referral is needed (TABLE 311). As such, HLA-B27 and CRP testing should be performed in all patients suspected of having an axSpA spectrum disorder.
Continue to: HLA-B27 is...