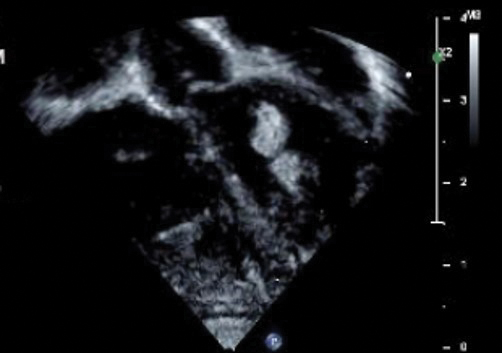
The pathophysiologic mechanism behind the natural involution of cardiac rhabdomyomas has not been fully elucidated. It has been hypothesized that these masses stem from the inability of rhabdomyoma cells to divide after birth due to their embryonic myocyte derivation. 4
According to the TSC diagnostic criteria from the Tuberous Sclerosis Complex International Consensus Group, at least 2 major features or 1 major and 2 minor features are required to make a definitive diagnosis of TSC. Cutaneous signs represent more than one-third of major features of TSC; almost all patients with TSC have skin findings. 5
Identification of pathogenic mutations in either TSC 1 (on chromosome 9q34.3, encoding for hamartin) or TSC 2 (on chromosome 16p13.3, encoding for tuberin), resulting in constitutive activation of mammalian target of rapamycin and subsequent increased cell growth, is sufficient for a definitive diagnosis of TSC. However, mutations cannot be identified by conventional genetic testing in as many as one-quarter of patients with TSC; therefore, a negative result does not exclude TSC if the patient meets clinical diagnostic criteria.
Although a cardiology workup is indicated prior to initiating propranolol in the presence of possible cardiac rhabdomyomas, most of those lesions are hemodynamically stable and do not require treatment. There also is no contraindication for β-blocker therapy. In fact, propranolol has been reported as a successful treatment in rhabdomyoma-associated arrhythmias in children. 6 Notably, obstructive cardiac rhabdomyomas have been successfully treated with mammalian target of rapamycin inhibitors, such as sirolimus 7 and everolimus. 8
Baseline cardiology screening with echocardiography prior to initiating propranolol for treatment of IH is not routinely indicated in babies with uncomplicated IH. However, in a patient with TSC, cardiology screening is necessary to rule out rhabdomyomas with associated arrhythmias or obstructed blood flow, or both, prior to initiating treatment.
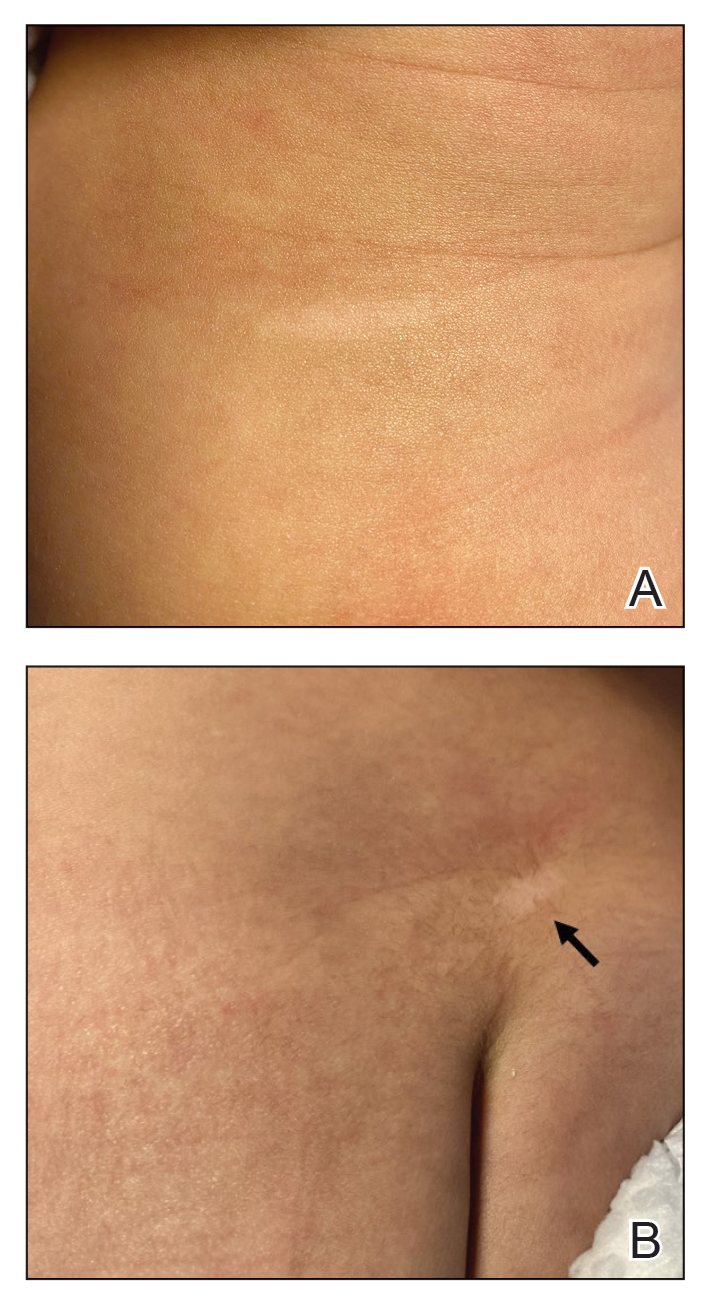
We presented a case of concomitant IH and TSC in a patient with cardiac rhabdomyomas. The manifestation of large IHs in our patient prompted further testing that revealed multiple cardiac rhabdomyomas in the context of TSC. It is imperative for cardiologists, cardiac surgeons, and dermatologists to be familiar with the TSC diagnostic criteria so that they can reach a prompt diagnosis and make appropriate referrals for further evaluation of cardiac, neurologic, and ophthalmologic signs.