Military Dermatology
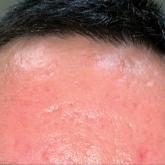
Fighting Acne for the Fighting Forces
Military servicemembers face unique challenges in the management of acne due to operational and medical readiness considerations.
Dr. Dunn is in private practice, Sarasota, Florida. Dr. Bandino is from the San Antonio Uniformed Services Health Education Consortium, Texas. Dr. Jarell is in private practice, Portsmouth, New Hampshire, and is affiliated with the Geisel School of Medicine at Dartmouth, Hanover, New Hampshire. Dr. Logemann is from the Naval Medical Center, San Diego, California. Dr. Miller is from Prevea Health, Kohler, Green Bay, and Sheboygan, Wisconsin.
The authors report no conflict of interest.
The views expressed in this article reflect the results of research conducted by the authors and do not necessarily reflect the official policy or position of the Department of the Navy, Department of Defense, or the US Government.
Correspondence: Justin P. Bandino, MD, 1100 Wilford Hall Loop, JBSA-Lackland, TX 78236 (tantomed@gmail.com).

Dr. Logemann: I’m definitely aware that we have different telehealth opportunities available, even using some newer modalities that are command approved in recent weeks. My experience has been for more complicated dermatology, so people are in remote locations, and they’re being seen by a nondermatologist, and they have questions about how to approach management. But I’m not aware of telemedicine as a screening tool for skin cancer in the military or among my civilian colleagues. I would hope that it could be someday because we’re developing these total-body photography machines as well. It could be a way for a nondermatologist who identifies a lesion to have it triaged by a dermatologist. To say, “Oh yeah, that looks like a melanoma. They need to get in sooner vs later,” but not on a large-scale sort of screening modality.
Dr. Bandino: In my recent experience, it has definitely been a helpful triage tool. In the military, this form of triage can be particularly helpful if someone is overseas to determine whether he/she needs to evacuated and evaluated in-person right away.
Dr. Jarell: It’s been useful in looking at benign things. People have shown me in the past few weeks a lot of seborrheic keratoses and a lot of benign dermal nevus-type things, and I say, “Don’t worry about that.” And you can tell if the resolution is good enough. But a lot of people have shown me things in the past few weeks that have clearly been basal cell carcinoma, which we can probably let that ride out for a few more weeks, but I’m not sure if maybe somebody has an amelanotic melanoma. Maybe you need to come in and get that biopsied ASAP. Or something that looks like a melanoma. The patient should probably come in and get that biopsied.
Dr. Miller: I think we can rely on teledermatology. It’s all predicated on the resolution because we’re all trained in pattern recognition. I think it’s very useful to screen for things that look clinically benign. We have to understand that most dermatology is practiced by nondermatologists in the United States, and many studies show that their diagnostic accuracy is 20%, at best maybe 50%. So, they do need to reach out to a dermatologist and perhaps get some guidance on what to do. I think it could be a very useful tool if used appropriately.
Dr. Dunn: If used appropriately, teledermatology could function in a couple of ways. One, it could allow us to declare lesions to be wholly benign, and only should a lesion change would it need attention. The second is that it would allow us to accelerate the process of getting a patient to us—physically in front of us—for a biopsy if a suspicious lesion is seen. A by-product of that process would be that if patients who have wholly benign, nonworrisome lesions could be screened by telemedicine, then physical appointments where a patient is in front of the doctor would be more open. In other words, let’s say if 25% of all lesional visits could be declared benign via telemedicine that would allow dermatology to preserve its face-to-face appointments for patients who are more likely to have cancer and require procedures like skin biopsy.

Military servicemembers face unique challenges in the management of acne due to operational and medical readiness considerations.
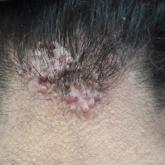
The active-duty military population faces unique challenges in the treatment of acne keloidalis nuchae because personal appearance and grooming...

Hyperbaric oxygen therapy can be considered for the treatment of failing cutaneous grafts and flaps, chronic ulcerations caused by vasculitis or...
