Case Reports
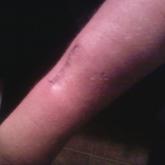
Muckle-Wells Syndrome in the Setting of Basal Cell Nevus Syndrome
Muckle-Wells syndrome (MWS) is a rare disorder inherited in an autosomal-dominant fashion that belongs to a group of hereditary periodic fever...
Dr. Shariff is from the University of New Mexico School of Medicine, Albuquerque. Dr. Hillerson is from the University of Kentucky Hospital, Lexington. Dr. Ross is from the University of Texas Medical Branch, Galveston. Dr. Ayala-Pena is from the University of Utah School of Medicine, Salt Lake City.
The authors report no conflict of interest.
Correspondence: Dustin Hillerson, MD, 900 S Limestone St, CTW 326, Lexington, KY 40536-0200 (dustin.hillerson@me.com).

After hospital admission, the patient’s mucosal desquamation progressively improved. By day 3, he required minimal supplemental oxygen with resolution of bowel symptoms and improved mucosal and skin findings. He was discharged on day 4 with supplemental oxygen and a 7-day course of prednisone, fluconazole, liquid oxycodone, pantoprazole, and acetaminophen. He showed continued improvement at a follow-up outpatient visit 2 days following discharge.
Stevens-Johnson syndrome is a rare severe drug reaction characterized by high fevers, mucosal erosions, tenderness, and skin detachment approximately 1 to 3 weeks after an inciting event.1,2 Although SJS has been linked to infections and less commonly to immunizations, in more than 80% of cases, SJS is strongly associated with a recent medication change.3 The classes of drugs that have been implicated in SJS most commonly include antibiotics, anticonvulsants, and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.4 Stevens-Johnson syndrome from drug reactions is not uncommon; however, SJS secondary to isolated albuterol use is rare.
Although it is presumed that albuterol was the key inciting factor in our patient’s case of SJS, it also is recognized that mucosal SJS can be associated with M pneumoniae infection. For this reason, we performed polymerase chain reaction for M pneumoniae as well as a chest radiograph to rule out this possibility. In addition, our patient had denied prolonged respiratory symptoms suggestive of a mycoplasma pneumonia infection, such as a prodrome of cough, myalgia, headache, sore throat, or fever. A report of 8 patients with documented SJS and M pneumoniae as well as a review of the literature also demonstrated a mean of 10 days of prodromal symptoms prior to the onset of mucosal lesions and/or a rash.5 However, mucosal SJS associated with mycoplasma pneumonia is an important clinical entity that should not be forgotten during the workup of a young patient with mucosal lesions or rash suggestive of SJS.
The exact etiology and mechanism of drug-induced SJS is not well understood at this time; however, evidence suggests that SJS is strongly linked to the host’s inability to detoxify drug metabolites.6,7 It has been postulated that SJS occurs secondary to a cell-mediated immune response, which activates cytotoxic T lymphocytes and subsequently results in keratinocyte apoptosis. Keratinocyte apoptosis occurs via the CD95-CD95 death receptor and soluble or membrane-bound ligand interaction.3,8,9 Stevens-Johnson syndrome is thought to occur from an interaction involving an HLA antigen–restricted presentation of drug metabolites to cytotoxic T cells, which can be further supported by evidence of strong genetic associations with HLA antigen alleles B15.02 and B58.01 in the cases of carbamazepine- and allopurinol-induced SJS, respectively.6,7 However, the genetic associations of specific HLA antigen alleles and polymorphisms with SJS and other cutaneous reactions is thought to be drug specific and HLA antigen subtype specific.7 Therefore, it is difficult to determine or correlate the clinical outcomes and manifestations of drug reactions in individualized patients. The precise mechanism of antigenicity of albuterol in initiating this cascade has not yet been determined. However, these investigations provide strong evidence for a correlation between specific HLA antigen haplotypes and occurrence of drug antigenicity resulting in SJS and other cutaneous reactions in susceptible patient populations.
Although the specific molecular pathway and etiology of SJS is not well delineated, pathology in combination with clinical correlation allows for diagnosis. Early-stage biopsies in SJS typically show apoptotic keratinocytes throughout the epidermis. Late-stage biopsies exhibit subepidermal blisters and full-thickness epidermal necrosis.1 Histopathology was performed on 4-mm punch biopsies of the chest and back and demonstrated full-thickness epidermal necrosis with neutrophils and a few dyskeratotic cells, likely representing a late stage of epidermal involvement. Given the predominance of neutrophils, other diagnostic considerations based solely on the biopsy results included contact dermatitis or phototoxic dermatitis. The remaining inflammatory infiltrate was sparse. Immunofluorescence was pan-negative.
This report illustrates a rare case of SJS from isolated albuterol use. This adverse drug reaction has not been well reported in the literature and may be an important consideration in the management of a patient with asthma.

Muckle-Wells syndrome (MWS) is a rare disorder inherited in an autosomal-dominant fashion that belongs to a group of hereditary periodic fever...
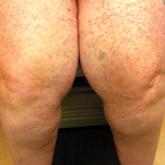
The mastocytoses comprise a group of proliferative stem cell disorders defined by the abnormal accumulation of mast cells (MCs) in the skin or...
