To the Editor:
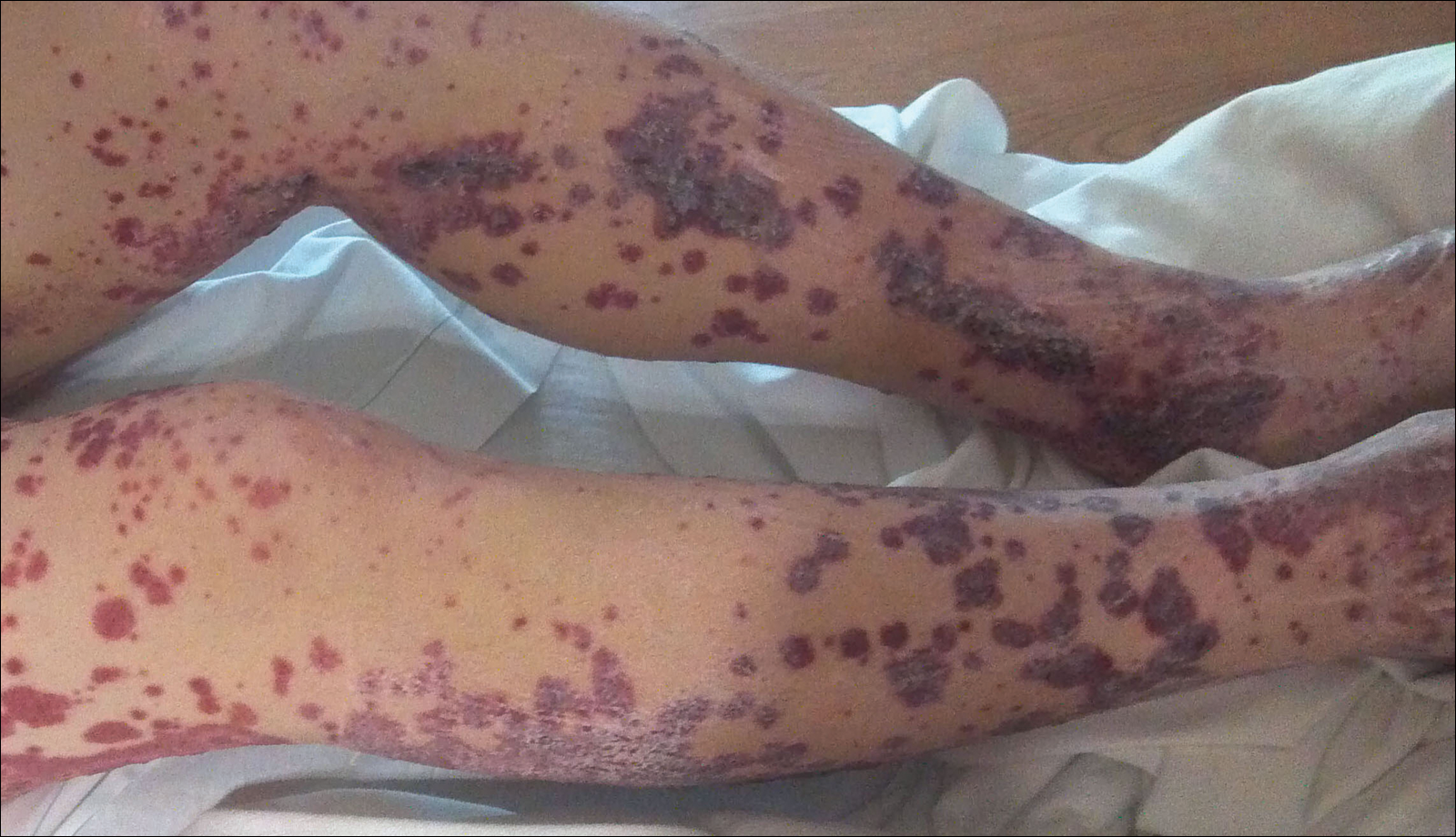
A 57-year-old man with a history of type 2 diabetes mellitus and hypertension was hospitalized for heart disease resulting in an aortic valve replacement and multiple-vessel bypass grafting. He experienced a stormy septic postoperative course during which he developed numerous palpable purplish plaques (Figure 1). The lesions were bilateral and more heavily involved the lower legs and buttocks. The head and neck remained free of skin lesions. Additionally, the patient reported a bilateral burning sensation from the knees to the feet.
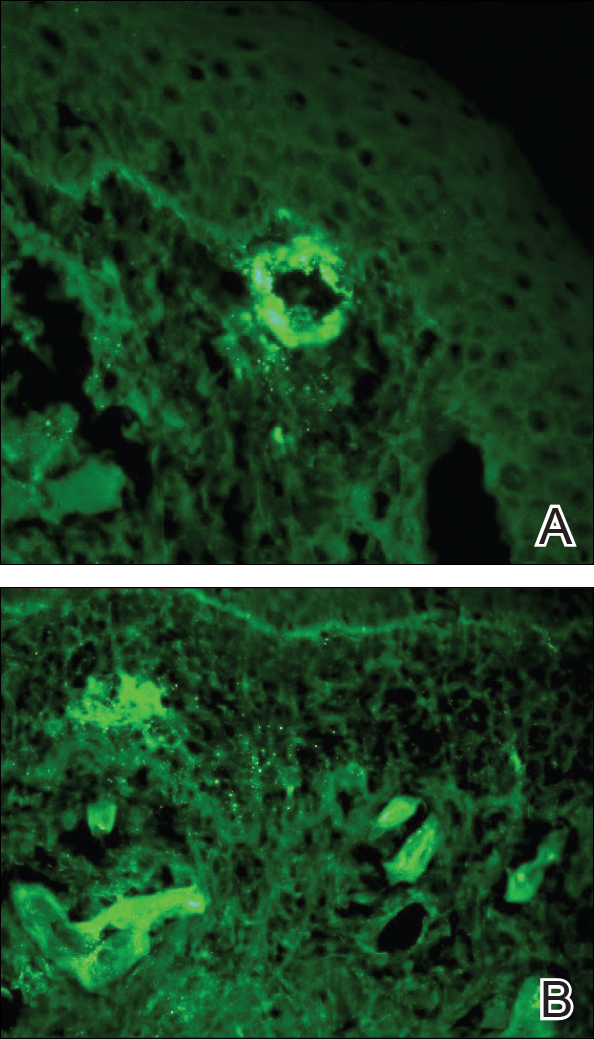
Punch biopsies of lesions from the right upper arm were obtained. Hematoxylin and eosin staining revealed neutrophilic-predominant small vessel vasculitis (Figure 2A) with the upper dermal location more heavily involved, as demonstrated by involvement of a superficial vascular plexus (Figures 2B and 2C) that was consistent with Henoch-Schönlein purpura (HSP). The diagnosis later was confirmed with immunofluorescence. Direct immunofluorescence revealed granular IgA deposition around the superficial vascular plexus (Figure 3). No IgG, IgM, C3, C5b-9 complement complex, or fibrinogen deposition was seen. Additionally, periodic acid-Schiff staining failed to show microorganisms, thrombi, or intravascular hyaline material.
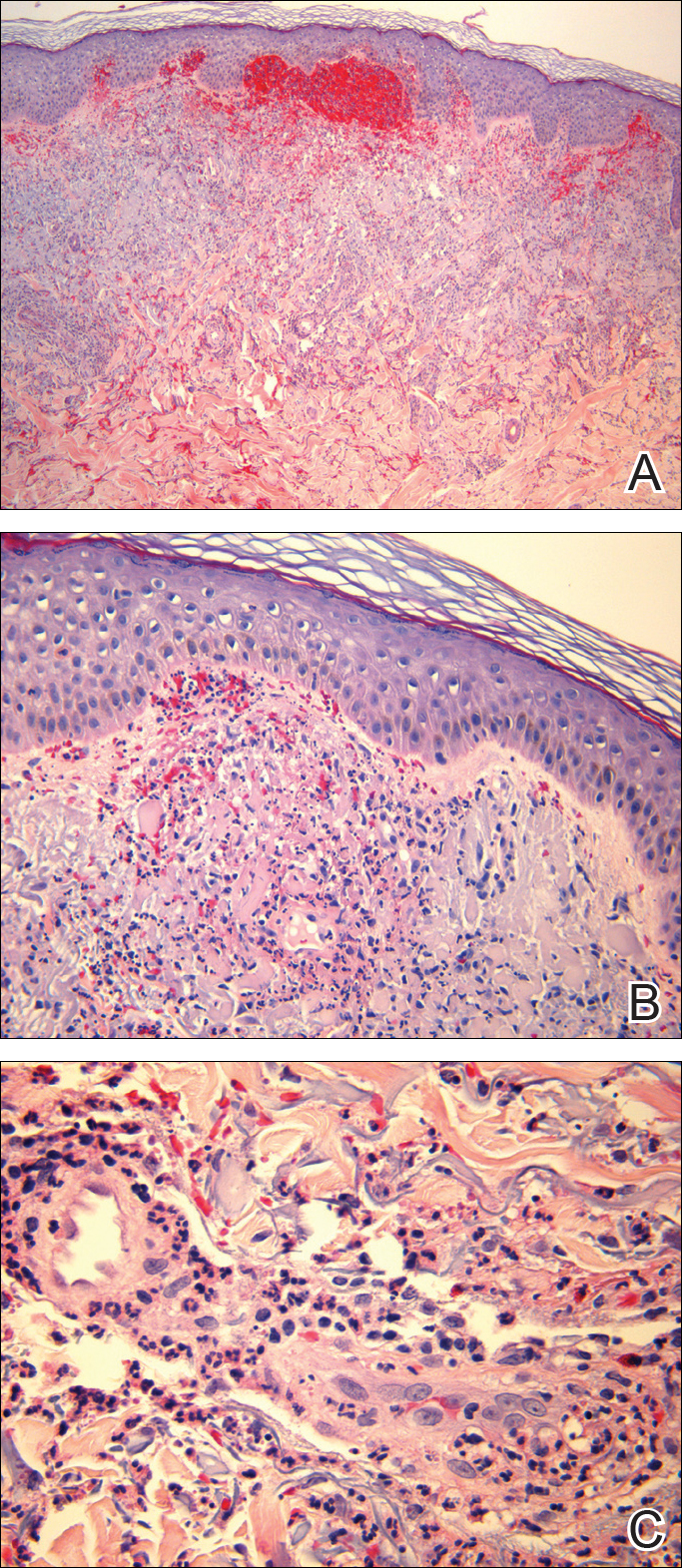
Figure 2. Henoch-Schönlein purpura. Acute neutrophilrich perivascular and interstitial inflammation with vascular disruption of superficial vascular plexus and red blood cell extravasation (A)(H&E, original magnification ×50). Early leukocytoclastic vasculitis of a papillary dermal vessel (B)(H&E, original magnification ×200). High magnification of a superficial vascular plexus with leukocytoclastic vasculitis with fibrinoid necrosis of the vessel wall (C)(H&E, original magnification ×400).
At our initial consultation, we observed an ill-appearing afebrile man with purplish plaques. Our impression was that he had vasculitis and not warfarin necrosis, which had been suspected by the cardiovascular team. The burning sensation noted by the patient lent credence to our vasculitic diagnosis. Proteinuria and hematuria were present; however, the values for blood urea nitrogen, creatinine, and glomerular filtration rate all remained within reference range. His signs and symptoms responded dramatically to prednisone. He remains on 1 mg of prednisone daily and a nephrologist continues to monitor renal function as an outpatient.